Opis ogólny
Protein X (UniProt: P69713; also known as HBx, Peptide X, pX) is encoded by the X gene (Gene ID: 944566) in Hepatitis B virus. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) contains seven main proteins, which include Core, pre-Core, Small S, Middle S, Large S, Polymerase, and the HBx protein. HBx, a multifunctional protein, although not essential for HBV infection, plays a role in silencing host antiviral defenses and promoting viral transcription. It facilitates the efficient replication of HBV by stimulating HBV gene expression from the cccDNA template. It is mainly localized in the cytoplasm with a small fraction detected in the nucleus. However, its expression level can also influence its cellular localization. It is predominantly nuclear when expressed in cells at very low levels but becomes largely cytoplasmic as its expression level increases. In cytoplasm, a minor fraction may also associate with mitochondria. Its mitochondrial targeting sequence is localized in amino acids 68-117. HBx has an N-terminal negative regulatory domain and its transactivation or coactivation of the C-terminal domain is reported to interfere with host cell signaling transduction pathways to help HBV replication. The best-characterized HBx binding partner is the cellular damage-specific DNA binding protein 1 (DDB1) and the interaction of HBx-DDB1 is essential for HBV replication. HBx promotes the degradation of the cellular structural maintenance of chromosomes 5/6 complex (Smc5/6), which directly binds DNA and entraps DNA plasmids. HBx is directly involved in development of cirrhosis and liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. (Ref.: Kornyeyev, D., et al. (2019). J. Virol. 93(16); e00248-19; Hwang, G-Y., et al. (2003). J. Clin. Microbiol. 41(12); 5598-5603).
Specyficzność
Reacts with Hbx-protein (trans-activator X gene product) of hepatitis B virus (epitope recognized - amino acid positions 90-115).
SPECIES REACTIVITIES:
Reacts only with HBV-infected human cells.
Immunogen
Epitope: X-Protein, aa 90-115
Peptide cooresponding to aa90-115 of h HBV-X protein.
Zastosowanie
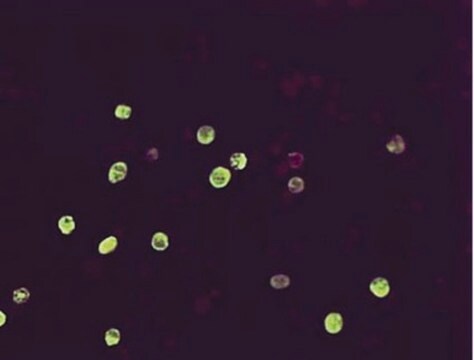
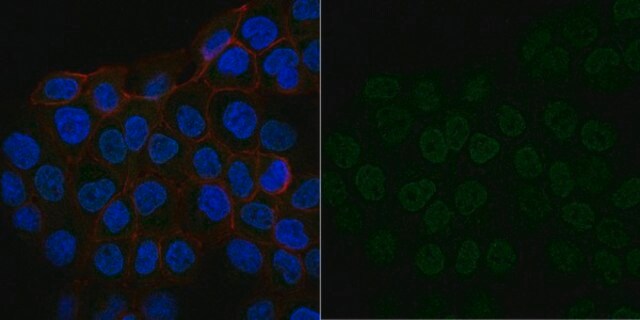
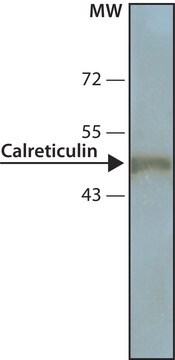
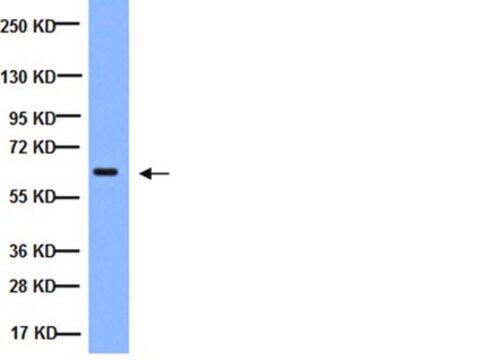
Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Antibody, X-Protein, a.a. 90-115, clone 227 detects level of Hepatitis B Virus & has been published & validated for use in ELISA, WB & IC.
ELISA, immunoblotting and immunocytochemistry staining of infected liver tissues and HBV-transfected hepatoma cells. Optimal working dilutions must be determined by the end user.
Research Category
Infectious Diseases
Research Sub Category
Infectious Diseases - Viral
Postać fizyczna
Format: Purified
Liquid in 0.02M PBS pH 7.6, 0.25M NaCl containing 0.1% sodium azide.
Przechowywanie i stabilność
Maintain at 2-8°C in undiluted aliquots for up to 12 months.
Inne uwagi
Concentration: Please refer to the Certificate of Analysis for the lot-specific concentration.
Informacje prawne
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Oświadczenie o zrzeczeniu się odpowiedzialności
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Ta strona może zawierać tekst przetłumaczony maszynowo.