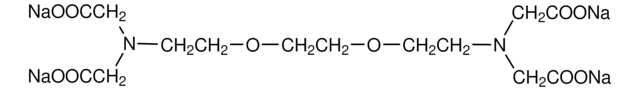616394
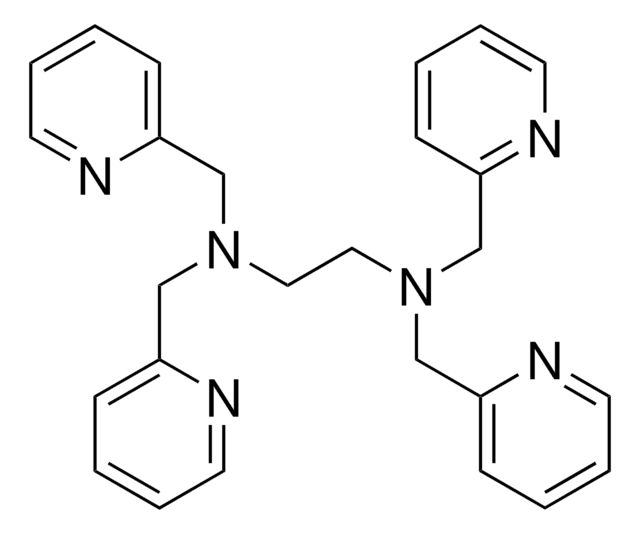
TPEN
Synonim(y):
TPEN, N,N,Nʹ,Nʹ- tetrakis-(2-Pyridylmethyl)ethylenediamine
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Próba
≥97% (titration)
Poziom jakości
Postać
solid
przydatność reakcji
reagent type: chelator
producent / nazwa handlowa
Calbiochem®
warunki przechowywania
OK to freeze
kolor
tan
rozpuszczalność
ethanol: 10 mg/mL
0.1 M phosphate pH 7.0: 25 μM
DMSO: soluble
Warunki transportu
ambient
temp. przechowywania
15-25°C
InChI
1S/C26H28N6/c1-5-13-27-23(9-1)19-31(20-24-10-2-6-14-28-24)17-18-32(21-25-11-3-7-15-29-25)22-26-12-4-8-16-30-26/h1-16H,17-22H2
Klucz InChI
CVRXLMUYFMERMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
- Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of p53 contributes to TPEN-induced neuronal apoptosis.: This study investigates the role of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of the tumor suppressor protein p53 in neuronal apoptosis induced by TPEN, highlighting mechanisms of cell death in neurodegenerative diseases (Kim HL et al., 2015).
- Essential role of p53 in TPEN-induced neuronal apoptosis.: This article explores the critical involvement of the p53 protein in apoptosis initiated by TPEN in neuronal cells, offering insights into potential therapeutic targets for neuroprotection (Ra H et al., 2009).
- Clioquinol induces autophagy in cultured astrocytes and neurons by acting as a zinc ionophore.: Demonstrates how Clioquinol, similar to TPEN, functions as a zinc ionophore to induce autophagy, particularly in neurological contexts, which may be relevant for understanding TPEN′s mechanisms (Park MH et al., 2011).
Ostrzeżenie
Rekonstytucja
Inne uwagi
Cherny, R.A., et al. 1999. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 23223.
Aballay, A., et al. 1995. Biochem. J.312, 919.
Jiang, S., et al. 1995. Lab. Invest.73, 111.
Sheridan, R.E. and Deshpande, S.S. 1995. Toxicon33, 539.
McCabe, M.J., et al. 1993. Lab. Invest. 69, 101.
Hinkle, P.M., et al. 1992. J. Biol. Chem.267, 25553.
Baba, A., et al. 1991. Brain Res. 557, 103.
Forbes, I.J., et al. 1991. Exp. Cell Res. 195, 224.
Csermely, P. and Somogyi, J. 1989. J. Cellular Physiol.138, 593.
Raspe, E., et al. 1989. Eur. J. Pharmacol.163, 345.
Arslan, L.P., et al. 1985. J. Biol. Chem.260, 2719.
Informacje prawne
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej