925217
TissueFab® - low endotoxin GelMA-UV bioink
0.2 μm filtered, suitable for 3D bioprinting applications
Synonim(y):
Bioink, GelMA, Metakrylamid żelatyny, Metakrylan żelatyny, Metakryloil żelatyny
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Poziom jakości
sterylność
0.2 μm filtered
Formularz
viscous liquid (to gel)
rozmiar
10 mL
zanieczyszczenia
≤5 CFU/g Bioburden
≤5 CFU/g Bioburden (Aerobic)
≤50 EU/mL Endotoxin
kolor
pale yellow to colorless
pH
6.5-7.5
lepkość
2-20 cP
Zastosowanie
3D bioprinting
temp. przechowywania
2-8°C
Powiązane kategorie
Opis ogólny
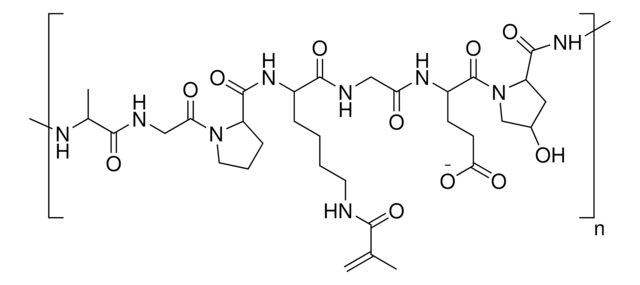
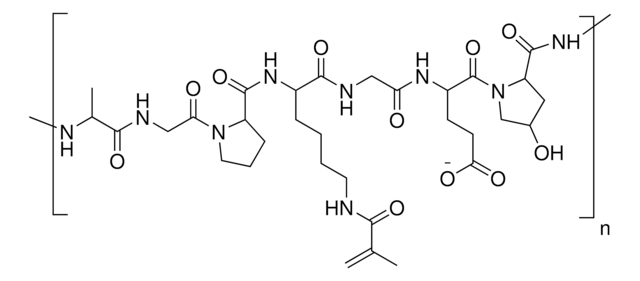
Dodanie fotosieciowalnych grup funkcyjnych metakrylamidu w GelMA pozwala na syntezę biokompatybilnych, biodegradowalnych i nieimmunogennych hydrożeli, które są stabilne w biologicznie istotnych warunkach i promują adhezję, rozprzestrzenianie się i proliferację komórek.
Czasową i przestrzenną kontrolę reakcji sieciowania można uzyskać poprzez dostosowanie stopnia funkcjonalizacji i warunków polimeryzacji, co pozwala na wytwarzanie hydrożeli o unikalnych wzorach, strukturach 3D i morfologiach.
Zastosowanie
- osteogenne,
- chondrogenne ,
- wątrobowe ,
- adipogenne ,
- naczyniotwórcze ,
- nabłonkowy ,
- śródbłonkowy ,
- zastawka serca ,
- skóra ,
- guzy
Cechy i korzyści
- Gotowa do użycia formuła zoptymalizowana pod kątem wysokiej wierności druku i żywotności komórek, eliminująca długotrwały proces opracowywania formuły biokomponentu.
- Protokoły krok po kroku opracowane i przetestowane przez naukowców MilliporeSigma 3D Bioprinting, bez konieczności posiadania wcześniejszego doświadczenia w bioprintingu 3D
- Odpowiedni dla różnych modeli biodrukarek 3D opartych na wytłaczaniu
- Grupa funkcyjna metakrylamidu może być również wykorzystywana do kontrolowania parametrów fizycznych hydrożelu, takich jak wielkość porów, szybkość degradacji i współczynnik pęcznienia.
Informacje prawne
Kod klasy składowania
10 - Combustible liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Dokumenty section.
Proszę o kontakt, jeśli potrzebna jest pomoc Obsługa Klienta
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej