Kluczowe dokumenty
851787
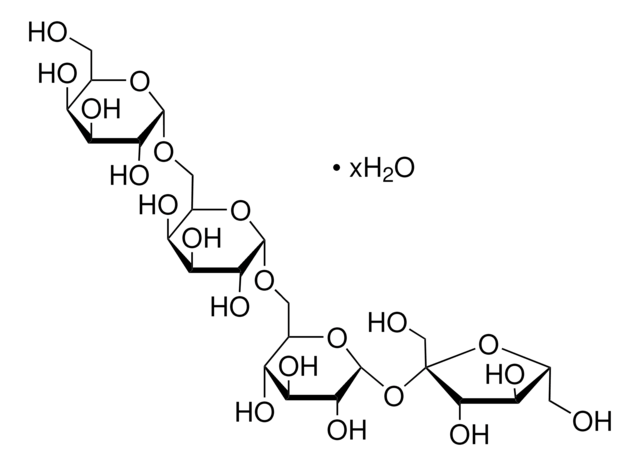
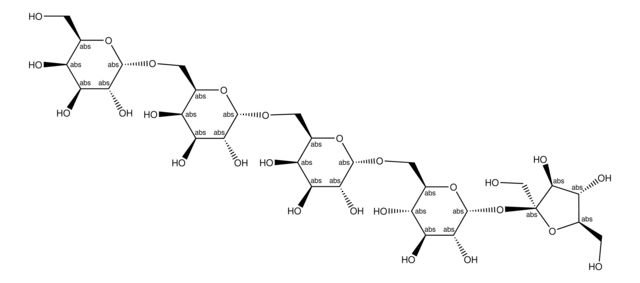
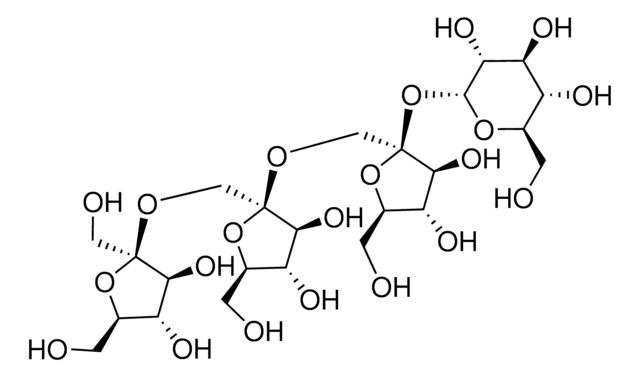
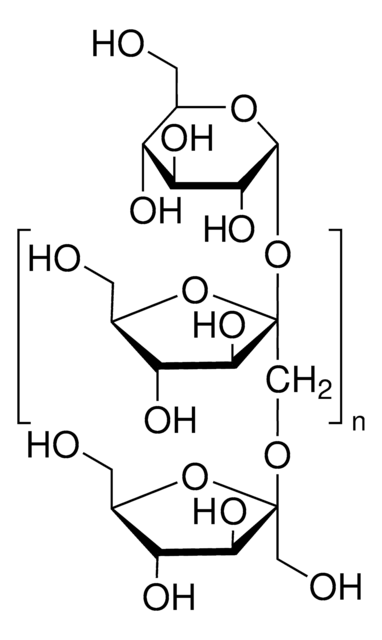
Stachyose hydrate
98%
Synonim(y):
α-D-Gal-(1→6)-α-D-Gal-(1→6)-α-D-Glc-(1→2)-β-D-Fru, β-D-Fructofuranosyl-O-α-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→6)-O-α-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→6)-α-D-glucopyranoside, Lupeose
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Próba
98%
Formularz
powder
aktywność optyczna
[α]24/D +133°, c = 4 in H2O
ciąg SMILES
O.OC[C@H]1O[C@H](OC[C@H]2O[C@H](OC[C@H]3O[C@H](O[C@]4(CO)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]4O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]3O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O
InChI
1S/C24H42O21.H2O/c25-1-6-10(28)14(32)17(35)21(41-6)39-3-8-11(29)15(33)18(36)22(42-8)40-4-9-12(30)16(34)19(37)23(43-9)45-24(5-27)20(38)13(31)7(2-26)44-24;/h6-23,25-38H,1-5H2;1H2/t6-,7-,8-,9-,10+,11+,12-,13-,14+,15+,16+,17-,18-,19-,20+,21+,22+,23-,24+;/m1./s1
Klucz InChI
YDBMRUQRXAFOAH-KTDNCYJLSA-N
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Zastosowanie
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej