Kluczowe dokumenty
746991
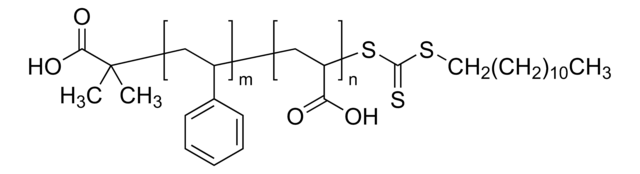
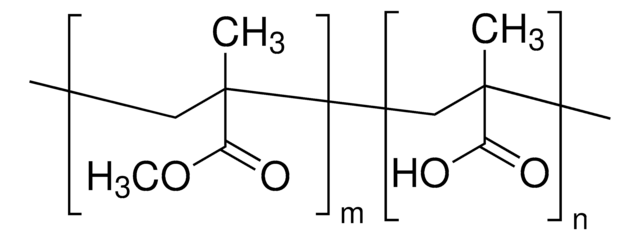
Polystyrene-block-poly(acrylic acid)
Synonim(y):
Poly(styrene)-block-poly(acrylic acid)
About This Item
Polecane produkty
Formularz
solid
masa cząsteczkowa
Mn 27,000-31,000 (polystyrene)
Mn 31,000-37,000 (total)
Mn 4,000-6,000 (poly(acrylic acid))
mp
258-263 °C
PDI
≤1.3
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Zastosowanie
Informacje prawne
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Warning
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organy docelowe
Respiratory system
Kod klasy składowania
11 - Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Nie widzisz odpowiedniej wersji?
Jeśli potrzebujesz konkretnej wersji, możesz wyszukać konkretny certyfikat według numeru partii lub serii.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Produkty
Polimeryzacja z odwracalną addycją i fragmentacją łańcucha (RAFT) szybko wysuwa się na pierwszy plan w konstrukcji nośników leków i genów.
Reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization is rapidly moving to the forefront in construction of drug and gene delivery vehicles.
Opracowanie leków ukierunkowanych na określone miejsca w ludzkim ciele pozostaje obecnie jednym z największych wyzwań w biomedycynie.
The development of drugs that target specific locations within the human body remains one of the greatest challenges in biomedicine today.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej