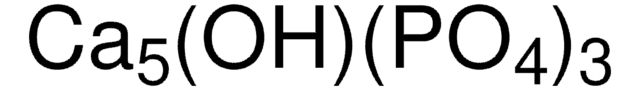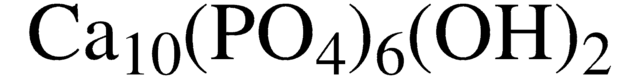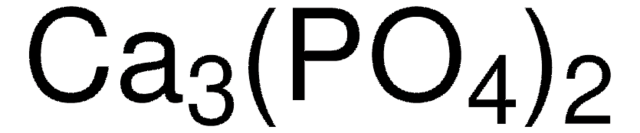Kluczowe dokumenty
677418
Hydroxyapatite
nanopowder, <200 nm particle size (BET), ≥97%, synthetic
Synonim(y):
Calcium phosphate tribasic, Calcium hydroxyphosphate, HAp, Hydroxylapatite, Tribasic calcium phosphate
About This Item
solid
Polecane produkty
Poziom jakości
Próba
≥97%
Formularz
nanopowder
solid
powierzchnia
>9.4 m2/g
wielkość cząstki
<200 nm (BET)
mp
1100 °C (lit.)
ciąg SMILES
[Ca++].[Ca++].[Ca++].[Ca++].O[Ca+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O
InChI
1S/5Ca.3H3O4P.H2O/c;;;;;3*1-5(2,3)4;/h;;;;;3*(H3,1,2,3,4);1H2/q5*+2;;;;/p-10
Klucz InChI
XYJRXVWERLGGKC-UHFFFAOYSA-D
Szukasz podobnych produktów? Odwiedź Przewodnik dotyczący porównywania produktów
Opis ogólny
Zastosowanie
Poly (sodium 4-styrene sulfonate)-modified hydroxyapatite nanoparticles can be used as a drug carrier for vancomycin. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles control the release of antibiotics after the implantation of a scaffold in the body.
Porous hydroxyapatite microspheres exhibit a high adsorptive capacity for heavy metals and can be used for the treatment of heavy metal contaminated water.
Cechy i korzyści
- Bioactive and biocompatible
- Good mechanical strength
- Porous structure
- Osteoconductive and osteointegrative properties
Informacje prawne
Kod klasy składowania
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 1
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Środki ochrony indywidualnej
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Wybierz jedną z najnowszych wersji:
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Produkty
Nanomateriały są wykorzystywane w wielu zastosowaniach biomedycznych, w tym w czujnikach DNA, nanokompozytach polimerowych do zastosowań ortopedycznych i nanostrukturalnych podłożach wspomagających przyczepianie i wzrost komórek w inżynierii tkankowej.
Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications
Innovation in dental restorative materials is driven by the need for biocompatible and natural-appearing restoration alternatives. Conventional dental materials like amalgam and composite resins have inherent disadvantages.
A key challenge for nanomaterial safety assessment is the ability to handle the large number of newly engineered nanomaterials (ENMs), including developing cost-effective methods that can be used for hazard screening.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej