おすすめの製品
由来生物
rabbit
品質水準
結合体
unconjugated
抗体製品の状態
IgG fraction of antiserum
抗体製品タイプ
primary antibodies
クローン
polyclonal
フォーム
buffered aqueous solution
化学種の反応性
mouse, human
テクニック
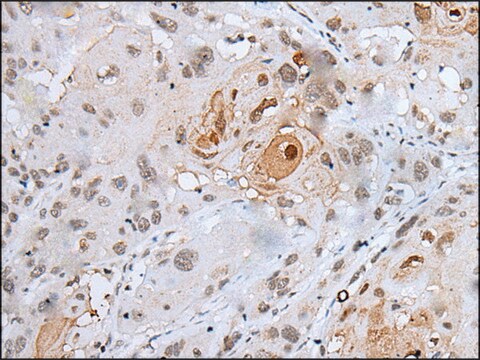
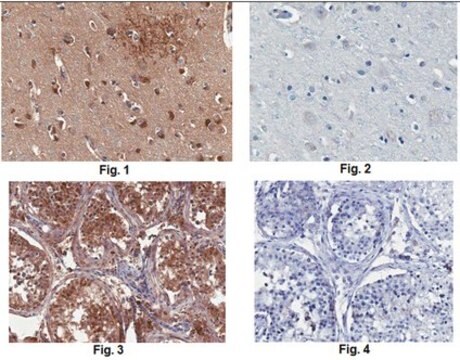
immunohistochemistry: 1:50-1:100
indirect ELISA: 1:1000
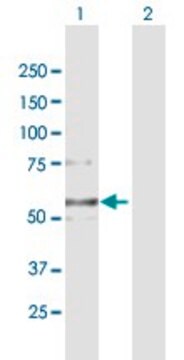
western blot: 1:100-1:500
NCBIアクセッション番号
輸送温度
dry ice
保管温度
−20°C
ターゲットの翻訳後修飾
unmodified
遺伝子情報
human ... MLCK(91807)
詳細
MLCK, a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family, is a calcium/calmodulin-dependent enzyme responsible for smooth muscle contraction via phosphorylation of a specific serine in the N-terminus of myosin light chains (MLC), an event that facilitates myosin interaction with actin filaments. It is a central determinant in the development of vascular permeability and tissue edema formation. In the nervous system it has been shown to control the growth initiation of astrocytic processes in culture and to participate in transmitter release at synapses formed between cultured sympathetic ganglion cells. MLCK acts as a critical participant in signaling sequences that result in fibroblast apoptosis. Smooth muscle and non-muscle isozymes are expressed in a wide variety of adult and fetal tissues and in cultured endothelium with qualitative expression appearing to be neither tissue- nor development-specific. Non-muscle isoform 2 is the dominant splice variant expressed in various tissues. The Telokin isoform, which binds calmodulin, has been found in a wide variety of adult and fetal tissues. MLCK is probably down-regulated by phosphorylation. The protein contains 1 fibronectin type III domain and 9 immunoglobulin-like C2-type domains.
Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is a serine/threonine kinase. It is encoded by the gene mapped to human chromosome 3q21.1. The encoded protein contains an N-terminal actin binding domain, a central kinase domain and C-terminal calmodulin and myosin-binding domains.
Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is a serine/threonine kinase. It is encoded by the gene mapped to human chromosome 3q21.1. The encoded protein contains an N-terminal actin binding domain, a central kinase domain and C-terminal calmodulin and myosin-binding domains.
Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is a serine/threonine kinase, encoded by the gene mapped to human chromosome 3q21.1. The protein contains immunoglobulin (Ig) repeats and fibronectin type 3 like repeats.
免疫原
MLCK (Q96DV1, 20-55)
This antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide selected from the N-terminal region of human MLCK.
This antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide selected from the N-terminal region of human MLCK.
アプリケーション
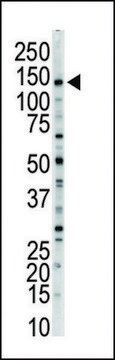
Anti-MLCK (N-term) antibody produced in rabbit has been used in Western blotting.
Anti-MLCK (N-term) antibody produced in rabbit has been used in Western blotting.
生物化学的/生理学的作用
Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is activated by the binding of Ca2+/calmodulin. It has a role in smooth muscle contraction. The kinase phosphorylates the regulatory light chain of smooth muscle myosin. This stimulates ATPase activity of the myosin heads and leads to the myosin power stroke, which is crucial for muscle contraction. MLCK also assists the interaction of myosin with actin. Loss of function of the protein has been linked to megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome. In nonmuscle cells, MLCK facilitates various functions such as the maintenance of endothelial cells permeability, stress fiber formation, cell migration, fibroblasts contractile activity and proliferation. It also aids in cytokinesis, secretion, neurite growth cone extension, modulation of ion channel currents. In addition, MLCK is also implicated in signaling pathways leading to fibroblast apoptosis and maintenance of normal cardiac function.
Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is activated by the binding of Ca2+/calmodulin. It has a role in smooth muscle contraction. The kinase phosphorylates the regulatory light chain of smooth muscle myosin. This stimulates ATPase activity of the myosin heads and leads to the myosin power stroke, which is crucial for muscle contraction. MLCK also assists the interaction of myosin with actin. Loss of function of the protein has been linked to megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome. It facilitates actin binding activity and regulates the actin–myosin interaction.
物理的形状
精製済みポリクローナル抗体のPBS溶液(0.09%(W/V)アジ化ナトリウム含有)
免責事項
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
適切な製品が見つかりませんか。
製品選択ツール.をお試しください
保管分類コード
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
nwg
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
SAB1300116-VAR:
SAB1300116-100UG:
SAB1300116-BULK:
最新バージョンのいずれかを選択してください:
Alexander García Ponce et al.
Scientific reports, 6, 29003-29003 (2016-07-01)
Changes in vascular permeability occur during inflammation and the actin cytoskeleton plays a crucial role in regulating endothelial cell contacts and permeability. We demonstrated recently that the actin-binding protein cortactin regulates vascular permeability via Rap1. However, it is unknown if
A novel variant in MYLK causes thoracic aortic dissections: genotypic and phenotypic description.
Hannuksela M, et al.
BMC Medical Genetics, 17(1), 61-61 (2016)
Mutation analysis of the non?muscle myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) deletion constructs on CV1 fibroblast contractile activity and proliferation
Wadgaonkar R, et al.
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 88(3), 623-634 (2003)
Loss-of-function variants in MYLK cause recessive megacystis microcolon intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome.
Halim D, et al.
American Journal of Human Genetics, 101(1), 123-129 (2017)
Increasing evidence of mechanical force as a functional regulator in smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase.
Baumann F, et al.
eLife, 6 (2017)
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)