About This Item
おすすめの製品
アッセイ
≥98% (HPLC)
フォーム
powder
光学活性
[α]25/D −24 to −26°, c = 5 in H2O(lit.)
色
white to off-white
mp
195-199 °C (dry matter) (lit.)
溶解性
H2O: 50 mg/mL
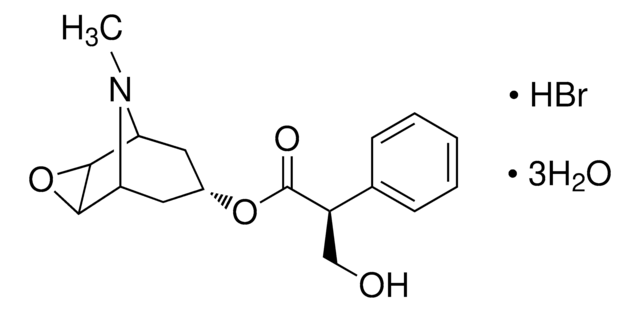
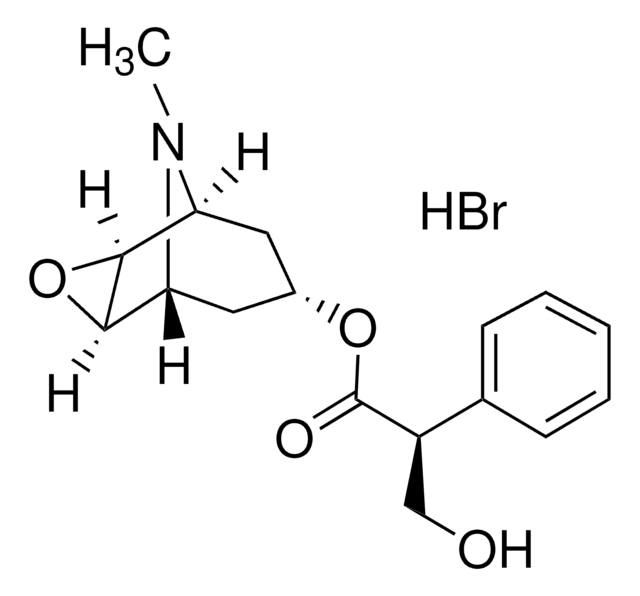
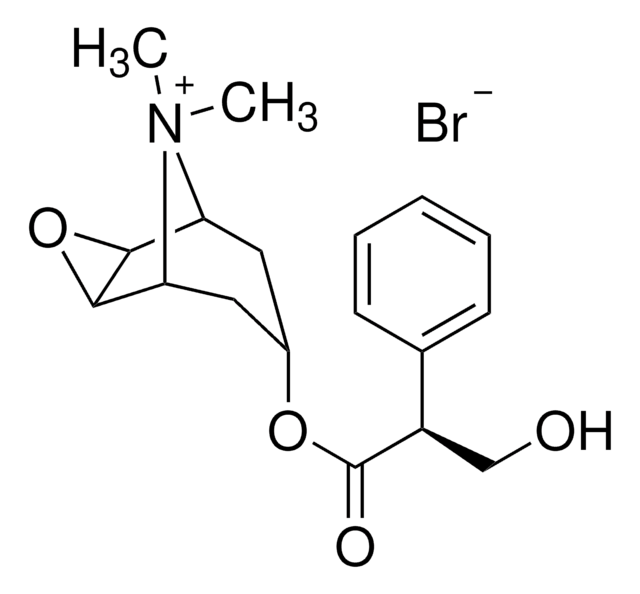
SMILES記法
O.O.O.Br.CN1[C@@H]2C[C@H](C[C@H]1[C@@H]3O[C@H]23)OC(=O)[C@H](CO)c4ccccc4
InChI
1S/C17H21NO4.BrH.3H2O/c1-18-13-7-11(8-14(18)16-15(13)22-16)21-17(20)12(9-19)10-5-3-2-4-6-10;;;;/h2-6,11-16,19H,7-9H2,1H3;1H;3*1H2/t11-,12-,13-,14+,15-,16+;;;;/m1..../s1
InChI Key
LACQPOBCQQPVIT-SEYKEWMNSA-N
遺伝子情報
human ... CHRM1(1128) , CHRM2(1129) , CHRM3(1131) , CHRM4(1132) , CHRM5(1133)
類似した製品をお探しですか? 訪問 製品比較ガイド
関連するカテゴリー
生物化学的/生理学的作用
特徴および利点
シグナルワード
Danger
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Acute Tox. 1 Dermal - Acute Tox. 2 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 2 Oral
保管分類コード
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 1
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
個人用保護具 (PPE)
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
S1875-5G:
S1875-VAR:
S1875-25G:
S1875-1G:
S1875-BULK:
この製品を見ている人はこちらもチェック
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)