すべての画像(1)
About This Item
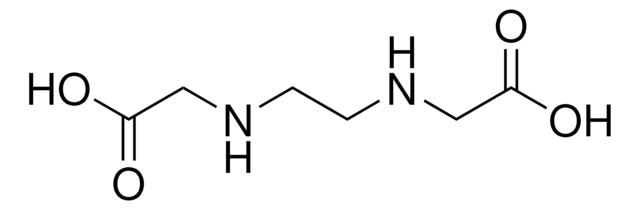
実験式(ヒル表記法):
C4H10N2O2
CAS番号:
分子量:
118.13
MDL番号:
UNSPSCコード:
12352106
PubChem Substance ID:
おすすめの製品
フォーム
powder
SMILES記法
NCCNCC(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H10N2O2/c5-1-2-6-3-4(7)8/h6H,1-3,5H2,(H,7,8)
InChI Key
PIINGYXNCHTJTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
その他情報
Please note that Sigma-Aldrich provides this product to early discovery researchers as part of a collection of unique chemicals. Sigma-Aldrich does not collect analytical data for this product. Buyer assumes responsibility to confirm product identity and/or purity. All sales are final.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY CONTRARY PROVISION CONTAINED IN SIGMA-ALDRICH′S STANDARD TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE OR AN AGREEMENT BETWEEN SIGMA-ALDRICH AND BUYER, SIGMA-ALDRICH SELLS THIS PRODUCT "AS-IS" AND MAKES NO REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY WHATSOEVER WITH RESPECT TO THIS PRODUCT, INCLUDING ANY (A) WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY; (B) WARRANTY OF FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE; OR (C) WARRANTY AGAINST INFRINGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS OF A THIRD PARTY; WHETHER ARISING BY LAW, COURSE OF DEALING, COURSE OF PERFORMANCE, USAGE OF TRADE OR OTHERWISE.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY CONTRARY PROVISION CONTAINED IN SIGMA-ALDRICH′S STANDARD TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE OR AN AGREEMENT BETWEEN SIGMA-ALDRICH AND BUYER, SIGMA-ALDRICH SELLS THIS PRODUCT "AS-IS" AND MAKES NO REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY WHATSOEVER WITH RESPECT TO THIS PRODUCT, INCLUDING ANY (A) WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY; (B) WARRANTY OF FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE; OR (C) WARRANTY AGAINST INFRINGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS OF A THIRD PARTY; WHETHER ARISING BY LAW, COURSE OF DEALING, COURSE OF PERFORMANCE, USAGE OF TRADE OR OTHERWISE.
シグナルワード
Warning
危険有害性情報
危険有害性の分類
Eye Irrit. 2
保管分類コード
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
CDS000144-250MG:
最新バージョンのいずれかを選択してください:
Sandra Anne Banack et al.
Neurotoxicity research, 33(1), 184-191 (2017-05-06)
β-N-Methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) is a non-canonical amino acid implicated as a cause for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism dementia complex and potentially other neurodegenerative diseases. As interest in this molecule has increased, there has been a proliferation of methods along with a plethora
J S Metcalf et al.
Amino acids, 49(8), 1427-1439 (2017-06-18)
Chronic dietary exposure to the cyanobacterial toxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) triggers neuropathology in non-human primates, providing support for the theory that BMAA causes a fatal neurodegenerative illness among the indigenous Chamorro people of Guam. However, since there are two stereoisomers of
Sung Vo Duy et al.
PloS one, 14(8), e0220698-e0220698 (2019-08-07)
The neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA), suspected to trigger neurodegenerative diseases, can be produced during cyanobacterial bloom events and subsequently affect ecosystems and water sources. Some of its isomers including β-amino-N-methylalanine (BAMA), N-(2-aminoethyl) glycine (AEG), and 2,4-diaminobutyric acid (DAB) may show different
Zacharias J Smith et al.
Toxins, 12(9) (2020-09-03)
Chautauqua Lake, New York, is a two-basin lake with a deeper, cooler, and less nutrient-rich Northern Basin, and a warmer, shallower, nutrient-replete Southern Basin. The lake is populated by a complex mixture of cyanobacteria, with toxigenic strains that produce microcystins
Daniel G Beach et al.
Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry, 407(28), 8397-8409 (2015-09-24)
The neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) has been reported in cyanobacteria and shellfish, raising concerns about widespread human exposure. However, inconsistent results for BMAA analysis have led to controversy. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) is the most appropriate method for analysis of
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)
![4-[(3-aminopropyl)amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid AldrichCPR](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/209/799/796e70c9-d7f0-4443-ba30-e905b78e049d/640/796e70c9-d7f0-4443-ba30-e905b78e049d.png)