おすすめの製品
詳細
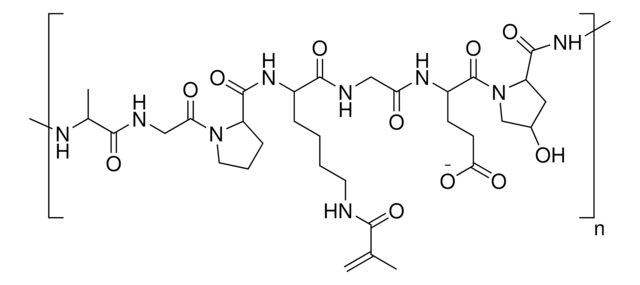
TissueFab® bioink -(GelAlgHA)MA Vis/405 nm, low endotoxin formulation is derived from natural polymers – hyaluronic acid, alginate, and gelatin. This ready to print bioink is optimized for 3D bioprinting of tissues and constructs using an extrusion-based 3D bioprinter. TissueFab® bioink -(GelAlgHA)MA Vis/405 nm, low endotoxin formulation can be used to bioprint cell-laden hydrogels in the desired shape without any supporting material and can be crosslinked in one step using exposure to UV light for further culture and maturation of cells for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications.
3D bioprinting is the printing of biocompatible materials, cells, growth factors, and the other supporting materials necessary to yield functional complex living tissues. Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) is a polymerizable hydrogel material derived from natural extracellular matrix (ECM) components. Due to its low cost, abundance, and retention of natural cell binding motifs, gelatin has become a highly sought material for tissue engineering applications. Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a linear polysaccharide of alternating D-glucuronic acid, and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine found in the extracellular matrix. HA is commonly chemically modified to form covalently crosslinked hydrogels. Alginate methacryloyl also known as AlgMA, is a polysaccharide widely used in tissue engineering obtained from brown algae.
3D bioprinting is the printing of biocompatible materials, cells, growth factors, and the other supporting materials necessary to yield functional complex living tissues. Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) is a polymerizable hydrogel material derived from natural extracellular matrix (ECM) components. Due to its low cost, abundance, and retention of natural cell binding motifs, gelatin has become a highly sought material for tissue engineering applications. Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a linear polysaccharide of alternating D-glucuronic acid, and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine found in the extracellular matrix. HA is commonly chemically modified to form covalently crosslinked hydrogels. Alginate methacryloyl also known as AlgMA, is a polysaccharide widely used in tissue engineering obtained from brown algae.
アプリケーション
3D bioprinting has been used to generate several different types of tissue such as skin, bone, vascular grafts, and cartilage structures. Based upon the desired properties, different materials and formulations can be used to generate both hard and soft tissues. While several 3D printing methods exist, due to the sensitivity of the materials used, extrusion-based methods with bioinks are most commonly employed.
Low Endotoxin, low bioburden: Endotoxins have been demonstrated negatively impact cellular growth, morphology, differentiation, inflammation and protein expression. Bioburden is defined as the number of contaminated organisms found in a given amount of material. We test each lot for endotoxins as well as total bioburden (aerobic and fungal) to minimize unwanted interactions. For more information: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/technical-documents/technical-article/microbiological-testing/pyrogen-testing/what-is-endotoxin
Low Endotoxin, low bioburden: Endotoxins have been demonstrated negatively impact cellular growth, morphology, differentiation, inflammation and protein expression. Bioburden is defined as the number of contaminated organisms found in a given amount of material. We test each lot for endotoxins as well as total bioburden (aerobic and fungal) to minimize unwanted interactions. For more information: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/technical-documents/technical-article/microbiological-testing/pyrogen-testing/what-is-endotoxin
包装
10 mL in HDPE bottle
法的情報
TISSUEFAB is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
保管分類コード
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
927252-VAR:
927252-BULK:
927252-10ML:
最新バージョンのいずれかを選択してください:
Emily Abelseth et al.
ACS biomaterials science & engineering, 5(1), 234-243 (2019-01-14)
3D bioprinting offers the opportunity to automate the process of tissue engineering, which combines biomaterial scaffolds and cells to generate substitutes for diseased or damaged tissues. These bioprinting methods construct tissue replacements by positioning cells encapsulated in bioinks into specific
N Laurens et al.
Journal of thrombosis and haemostasis : JTH, 4(5), 932-939 (2006-05-13)
Fibrinogen and fibrin play an important role in blood clotting, fibrinolysis, cellular and matrix interactions, inflammation, wound healing, angiogenesis, and neoplasia. The contribution of fibrin(ogen) to these processes largely depends not only on the characteristics of the fibrin(ogen) itself, but
Y Shi et al.
Biomedical materials (Bristol, England), 13(3), 035008-035008 (2018-01-09)
Three-dimensional bioprinting is an emerging technology for fabricating living 3D constructs, and it has shown great promise in tissue engineering. Bioinks are scaffold materials mixed with cells used by 3D bioprinting to form a required cell-laden structure. In this paper
Wanjun Liu et al.
Advanced healthcare materials, 6(12) (2017-05-04)
Bioprinting is an emerging technique for the fabrication of 3D cell-laden constructs. However, the progress for generating a 3D complex physiological microenvironment has been hampered by a lack of advanced cell-responsive bioinks that enable bioprinting with high structural fidelity, particularly
B Duan et al.
Acta biomaterialia, 10(5), 1836-1846 (2013-12-18)
Tissue engineering has great potential to provide a functional de novo living valve replacement, capable of integration with host tissue and growth. Among various valve conduit fabrication techniques, three-dimensional (3-D) bioprinting enables deposition of cells and hydrogels into 3-D constructs
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)