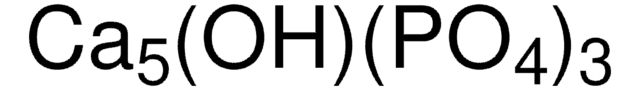702153
ヒドロキシアパタイト
nanoparticles, dispersion, 10 wt. % in H2O, <200 nm particle size (BET)
別名:
Calcium hydroxide phosphate, Calcium hydroxylapatite, Calcium hydroxyphosphate, Nano hydroxyapatatite, Pentacalcium hydroxide triphosphate
About This Item
おすすめの製品
形状
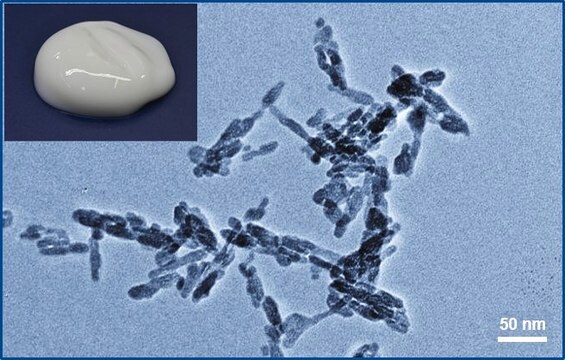
dispersion
nanoparticles
含みます
≤0.025 wt. % dispersant (non-metal based)
濃度
10 wt. % in H2O
表面積
14.3 m2/g , typical
粒径
<200 nm (BET)
pH
4-6
密度
1.038 g/mL at 25 °C
SMILES記法
[Ca++].[Ca++].[Ca++].[Ca++].O[Ca+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O
InChI
1S/5Ca.3H3O4P.H2O/c;;;;;3*1-5(2,3)4;/h;;;;;3*(H3,1,2,3,4);1H2/q5*+2;;;;/p-10
InChI Key
XYJRXVWERLGGKC-UHFFFAOYSA-D
類似した製品をお探しですか? 訪問 製品比較ガイド
詳細
アプリケーション
- 骨の無機成分と化学的に類似していることおよび骨誘導特性を有することから、 骨代替品のインプラント材料。
- カプセル化能といくつかの薬物およびタンパク質に対する親和性があるため、遺伝子および 薬物送達用の媒体。
- pH応答性粒子状乳化剤。
特徴および利点
- 生体適合性
- 骨伝導性
- 生理学的条件下で 安定
- 高い機械的強度
法的情報
保管分類コード
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
引火点(°F)
Not applicable
引火点(℃)
Not applicable
適用法令
試験研究用途を考慮した関連法令を主に挙げております。化学物質以外については、一部の情報のみ提供しています。 製品を安全かつ合法的に使用することは、使用者の義務です。最新情報により修正される場合があります。WEBの反映には時間を要することがあるため、適宜SDSをご参照ください。
Jan Code
702153-25ML:
702153-BULK:
702153-VAR:
試験成績書(COA)
製品のロット番号・バッチ番号を入力して、試験成績書(COA) を検索できます。ロット番号・バッチ番号は、製品ラベルに「Lot」または「Batch」に続いて記載されています。
資料
Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications
A key challenge for nanomaterial safety assessment is the ability to handle the large number of newly engineered nanomaterials (ENMs), including developing cost-effective methods that can be used for hazard screening.
ライフサイエンス、有機合成、材料科学、クロマトグラフィー、分析など、あらゆる分野の研究に経験のあるメンバーがおります。.
製品に関するお問い合わせはこちら(テクニカルサービス)