P4069
Phosphatase, Alkaline from Escherichia coli
buffered aqueous glycerol solution, 20-50 units/mg protein (in glycine buffer)
Sinonimo/i:
Orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase (alkaline optimum)
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
Escherichia coli
Livello qualitativo
Stato
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
Attività specifica
20-50 units/mg protein (in glycine buffer)
Attività estranea
DNase, RNase, none detected
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Applicazioni
Alkaline phosphatase is used for conjugation to antibodies and other proteins for ELISA, Western blotting, and histochemical detection. It may be used for protein labeling when high sensitivity is required. Product P4069 is provided as a buffered aqueous glycerol solution.
Phosphatase, Alkaline from Escherichia coli has been used:
- in fluorometric assay to determine its enzyme activity
- in the dephosphorylating enzyme cocktail for dephosphorylation of peptides
- in treating the nerve and HL60 cell lysate for β-hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase activity
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Alkaline phosphatase is a model enzyme for understanding phosphomonoesterase. It is used in various biochemical methods and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Alkaline phosphatase, from Escherichia coli, is a dimeric, non-glycosylated protein which mainly reside in the periplasmic space. Three known isoforms exist. The enzyme requires zinc, and is activated by magnesium. E. coli akaline phosphatase has a broad specificity for phosphate esters.
Avvertenza
Alkaline phosphatase in 5 mM EDTA, pH 8, will be irreversibly heat inactivated at 75°C for 10 minutes.
Definizione di unità
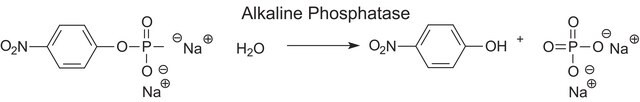
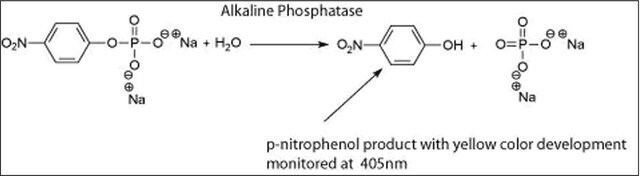
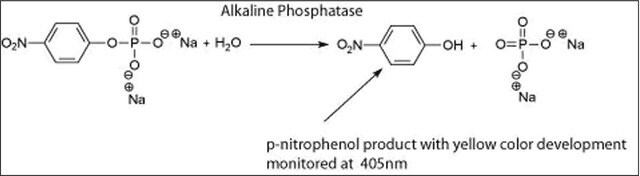
One unit will hydrolyze 1.0 μmole of p-nitrophenyl phosphate per min at pH 10.4 at 37 °C.
Stato fisico
Solution in 5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 0.5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM ZnCl2, 50% (w/v) glycerol
Risultati analitici
Protein determined by biuret.
Inibitore
Prodotti correlati
N° Catalogo
Descrizione
Determinazione del prezzo
Substrato
N° Catalogo
Descrizione
Determinazione del prezzo
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Resp. Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Phospho-iTRAQ data article: Assessing isobaric labels for the large-scale study of phosphopeptide stoichiometry
Glibert P, et al.
Data in Brief, 4(2), 60-65 (2015)
Sensitive fluorogenic substrate for alkaline phosphatase
Levine MN and Raines RT
Analytical Biochemistry, 418(2), 247-252 (2011)
The prion protein and cellular cholesterol homeostasis
Diomede L, et al.
Neurobiology of Lipids, 1(2), 8-14 (2002)
Lionel M Igaz et al.
The American journal of pathology, 173(1), 182-194 (2008-06-07)
TAR DNA-binding protein (TDP-43) has been recently described as a major pathological protein in both frontotemporal dementia with ubiquitin-positive inclusions (FTLD-U) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. However, little is known about the relative abundance and distribution of different pathological TDP-43 species
Jong Kil Lee et al.
The Journal of experimental medicine, 211(8), 1551-1570 (2014-07-23)
In Alzheimer's disease (AD), abnormal sphingolipid metabolism has been reported, although the pathogenic consequences of these changes have not been fully characterized. We show that acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) is increased in fibroblasts, brain, and/or plasma from patients with AD and
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.