A9460
Annexin V from human placenta
≥90% (SDS-PAGE), buffered aqueous solution
Sinonimo/i:
Annexin V, Calphosbindin I, Lipocortin V, PAP-1
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Codice UNSPSC:
41106305
NACRES:
NA.32
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
human placenta
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
Stato
buffered aqueous solution
PM
33 kDa (four subunits)
tecniche
cell based assay: suitable
Impurezze
Human Source(HCV), tested negative
Solubilità
water: soluble
Compatibilità
suitable for molecular biology
N° accesso UniProt
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−70°C
Informazioni sul gene
human ... ANXA5(308)
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Research area: Apoptosis
Annexin V is a calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein. It is expressed in high concentration in cells with barrier functions, such as vascular endothelium, epithelial cells in bile ducts, placental trophoblasts, mammary ducts, renal tubules, and nasal epithelium.
Annexin V is a calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein. It is expressed in high concentration in cells with barrier functions, such as vascular endothelium, epithelial cells in bile ducts, placental trophoblasts, mammary ducts, renal tubules, and nasal epithelium.
Applicazioni
Annexin V from human placenta has been used:
- to verify the involvement of phosphatidylserine in adhesion using flow cytometry
- to test adhesion specificity of phosphatidylserine
- for synthesis of NIR700-Annexin-V imaging probe
- in dynamic light scattering (DLS) assay to test the effects of various treatments on virion aggregation
Azioni biochim/fisiol
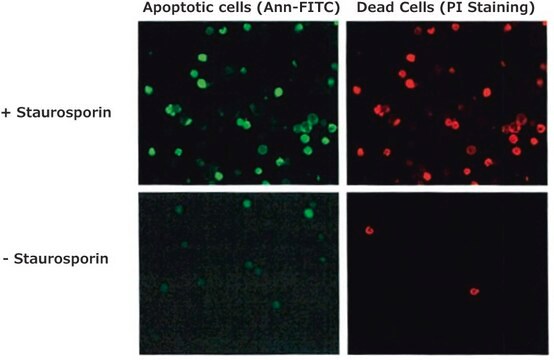
Annexins are ubiquitous homologous proteins that bind phospholipids in the presence of calcium. The cellular changes involved in the apoptotic process include loss of phospholipid asymmetry during the early stages. This phenomenon is universal and is not limited to stimulus or to mammalian cells, but also occurs in insect and plant cells. In living cells, phosphatidylserine is transported to the inside of the lipid bilayer by the Mg2+ATP dependent enzyme, aminophospholipid translocase. At the onset of apoptosis, phosphatidylserine becomes translocated to the external surface of the cell membrane. Since the movement of phosphatidylserine from the internal membrane surface to the external surface is an early indicator of apoptosis, annexin V and its conjugates that interact strongly and specifically with phosphatidylserine may be used to detect apoptosis. Annexin V conjugates can be used to detect apoptotic cells significantly earlier than DNA-based assays. Fluorescent dye labeled annexin V have applications in flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy, and laser scanning cytometry.
It is a widely used marker for identifying apoptotic cells due to its high affinity for phosphatidylserine, which is normally located on the inner leaflets of membranes but moves to the cell surface during programmed cell death.
Confezionamento
Package size based on protein content
Stato fisico
Solution in 40 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, containing 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT and 0.05% sodium azide.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 2
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
W J Buhl et al.
European journal of cell biology, 56(2), 381-390 (1991-12-01)
Membranes from human placenta contain proteins which inhibit the activity of phospholipases A2 by binding to phospholipid thus impeding substrate availability. We used unilamellar mixed liposomes and a partially purified cytosolic phospholipase A2 from placenta for characterizing this substrate-depleting activity.
B N Yamaja Setty et al.
Blood, 99(5), 1564-1571 (2002-02-28)
Phosphatidlyserine (PS) exposure on the erythrocyte surface endows the cell with the propensity of adhering to vascular endothelium. Because individuals with sickle cell disease (SCD) manifest loss of erythrocyte membrane asymmetry with PS exposure, we have assessed the contribution of
D D Schlaepfer et al.
Biochemistry, 31(6), 1886-1891 (1992-02-18)
Annexin V is a protein of unknown biological function that undergoes Ca(2+)-dependent binding to phospholipids located on the cytosolic face of the plasma membrane. Preliminary results presented herein suggest that a biological function of annexin V is the inhibition of
Yeast alcohol dehydrogenase: SH groups, disulfide groups, quaternary structure, and reactivation by reductive cleavage of disulfide groups.
M Bühner et al.
European journal of biochemistry, 11(1), 73-79 (1969-11-01)
Ke Chen et al.
Journal of biomedical science, 18, 57-57 (2011-08-17)
High glucose induced lipid synthesis leads to β cell glucolipotoxicity. Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) is reported to be partially involved in this process. Insulin induced gene-1 (Insig-1) is an important upstream regulator of Insig-1-SREBPs cleavage activating protein (SCAP)-SREBP-1c
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.