62316
Lipase from Candida rugosa
powder, yellow-brown, ≥2 U/mg
Sinonimo/i:
CCL
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
fungus (Candida rugosa)
Livello qualitativo
Forma fisica
powder
Attività specifica
≥2 U/mg
PM
Mr ~67000
Condizioni di stoccaggio
dry at room temperature
Concentrazione
≤100%
tecniche
analytical sample preparation: suitable
Colore
yellow-brown
Intervallo di pH
6.5—7.5 (0.01 g/L)
Solubilità
water: slightly soluble
applicazioni
sample preservation
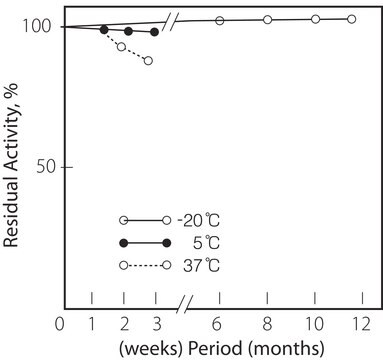
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
InChI
1S/C11H9N3O2.Na/c15-8-4-5-9(10(16)7-8)13-14-11-3-1-2-6-12-11;/h1-7,16H,(H,12,14);/q;+1/b13-9-;
QWZUIMCIEOCSJF-CHHCPSLASA-N
Informazioni sul gene
fungus ... LAP1(2544)
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
The lipase enzyme is a naturally occurring enzyme present in both the stomach and pancreatic juice. It is expressed and active in various tissues. For instance, hepatic lipases are found in the liver, hormone-sensitive lipases in adipocytes, lipoprotein lipase on the vascular endothelial surface, and pancreatic lipase in the small intestine. These lipases are classified within the alpha/beta-hydrolase fold superfamily of enzymes.
Applicazioni
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Definizione di unità
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Resp. Sens. 1
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.