67309
Kovac′s reagent for indoles
suitable for microbiology
Sinonimo/i:
4-(Dimethylamino)benzaldehyde solution
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
agenzia
according to ISO 16654:2001
Livello qualitativo
Nome Commerciale
BioChemika
Durata
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
Composizione
4-(dimethlyamino)benzaldehyde, 50 g/L
hydrochloric acid, 240 g/L
isoamylic alcohol, 710 g/L
tecniche
microbe id | specific enzyme detection: suitable
applicazioni
agriculture
clinical testing
environmental
food and beverages
microbiology
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Compatibilità
Escherichia coli
coliforms
Stringa SMILE
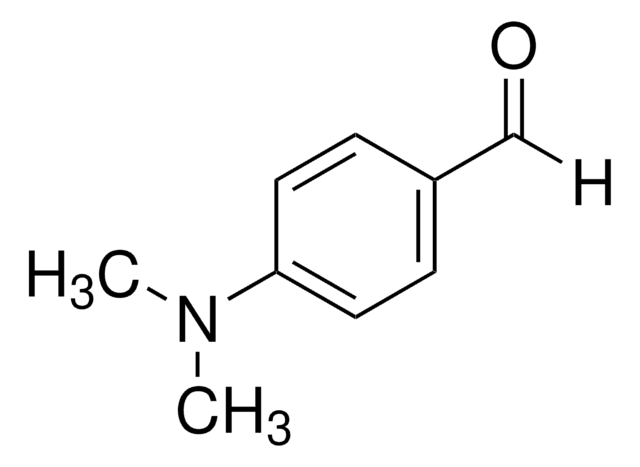
[H]C(=O)c1ccc(cc1)N(C)C
InChI
1S/C9H11NO/c1-10(2)9-5-3-8(7-11)4-6-9/h3-7H,1-2H3
BGNGWHSBYQYVRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Sostituito da
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Met. Corr. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
Organi bersaglio
Respiratory system
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
3 - Flammable liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
109.4 °F
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
43 °C
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
An article regarding the Role of Clostridium perfringens and their detection, identification, and differentiation from Sigma-Aldrich.com
For microbiologists the most fundamental stain was developed in 1884 by the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram.
Sigma-Aldrich.com presents an article concerning Differentiation of Escherichia coli from coliforms.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.