8.55079
DHP HM resin (100-200 mesh)
Novabiochem®
Sinonimo/i:
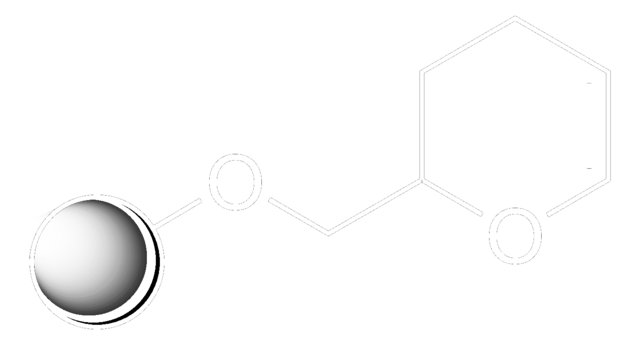
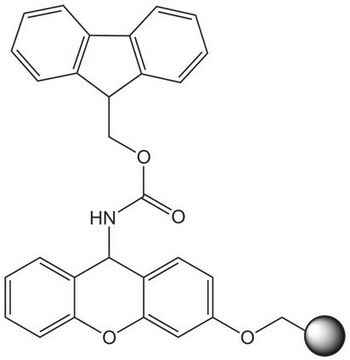
3,4-Dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl-methoxymethyl polystyrene (100-200 mesh), Ellman′s dihydropyran resin
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Nome Commerciale
Novabiochem®
Stato
beads
Impiego in reazioni chimiche
reaction type: Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis
reactivity: alcohol reactive
Produttore/marchio commerciale
Novabiochem®
applicazioni
peptide synthesis
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Descrizione generale
Associated Protocols and Technical Articles
Protocols for Loading of Peptide Synthesis Resins
Literature references
[1] L. A. Thompson & J. A. Ellman (1994) Tetrahedron Lett., 35, 9333.
[2] O. B. Wallace (1997) Tetrahedron Lett., 38, 4939.
[3] G. Liu & J. A. Ellman (1995) J. Org. Chem., 60, 7712.
[4] E. K. Kick & J. A. Ellman (1995) J. Med. Chem., 38, 1427.
[5] J. S. Koh & J. A. Ellman (1996) J. Org. Chem., 61, 4494.
[6] J. Cossy, et al. (2000) Synlett, 3, 409.
[7] M. Ramaseshan, et al. (2000) J. Comb. Chem., 2, 615.
[8] M. Ramaseshan, et al. (2000) Tetrahedron Lett., 41, 4743.
[9] A. Bianco, et al. (2000) J. Org. Chem., 65, 2179.
[10] M. Steger, et al. (2001) Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 11, 2537.
[11] A. Dahlgren, et al. (2003) Bioorg. Med.Chem. Lett., 11, 827.
[12] W. H. Pearson & R. B. Clark (1997) Tetrahedron Lett., 38, 7669.
[13] D. A. Nugiel, et al. (1997) J. Org. Chem., 62, 201.
[14] A. L. Smith, et al. (1998) Tetrahedron Lett., 39, 8317.
[15] S.-E. Yoo, et al. (1997) Tetrahedron Lett., 38, 1203.
[16] J. Beythien (Merck Biociences AG), personal communication.
[17] M. R. Tremblay, et al. (1999) Bioorg. Med . Chem. Lett., 9, 2827.
Linkage
Risultati analitici
Appearance of substance (visual): beads
Loading (determined from the substitution of the Fmoc-Gly-ol loaded resin): 0.70 - 1.20 mmol/g
Swelling Volume (in CH₂Cl₂): lot specific result
The polymer matrix is copoly (styrene-1% DVB), 100 - 200 mesh
Note legali
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.