810600P
Avanti
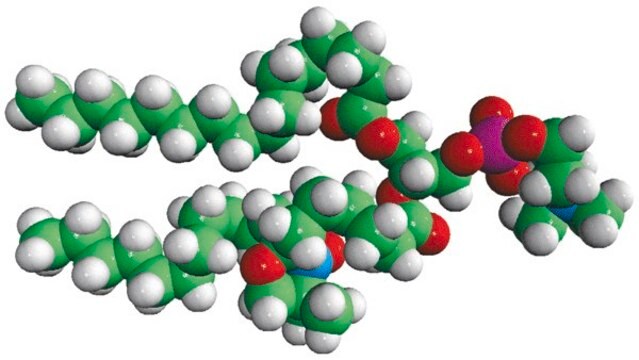
16:0-12 Doxyl PC
Avanti Research™ - A Croda Brand 810600P, powder
Sinonimo/i:
1-palmitoyl-2-stearoyl-(12-doxyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Formula empirica (notazione di Hill):
C46H90N2O10P
Numero CAS:
Peso molecolare:
862.19
Numero MDL:
Codice UNSPSC:
41141825
NACRES:
NA.25
Prodotti consigliati
Saggio
>99% (TLC)
Stato
powder
Confezionamento
pkg of 1 × 1 mg (810600P-1mg)
Produttore/marchio commerciale
Avanti Research™ - A Croda Brand 810600P
Tipo di lipide
ESR probes
phospholipids
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Descrizione generale
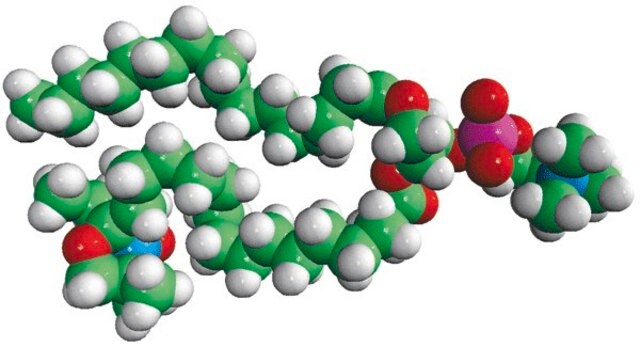
Avanti′s nitroxide spin product listing is a group of compounds designed to act as membrane probes. A variety of positions down the hydrophobic chain are labeled with the nitroxide functional groups to allow probing the membrane at various depths. These compounds have been synthesized from 1-palmitoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycerol-3-phosphocholine with the product being purified by column chromatography. Various n-doxyl phosphocholines have been recently used as biophysical tools to elucidate membrane trafficking with phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins and as fluorescent quenchers in lipid bilayer structural studies.
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is a strong bilayer-forming lipid. It the most common phospholipid in mammalian membranes. It is also an important component of the mucosal layer of the colon. 1-palmitoyl-2-stearoyl-(12-doxyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (12-NO-PC) is a nitroxide-labeled phospholipid.
Applicazioni
16:0-12 Doxyl PC is suitable for use:
- as a lipophilic collisional quencher to prepare liposomes used in lipophilic quenching experiments
- to prepare liposomes used in nitroxide quenching experiments to examine the location of each NBD (7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole) probe in mutants
- as a component in POPC or 1:1 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC)/1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-rac-1-glycerol (POPG) mixtures to prepare unlabelled large unilamellar liposomes
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) functions as a surfactant within the mucus to form a hydrophobic surface to inhibit bacterial penetrance. It is used to treat fat embolism. Phosphatidylcholine lowers the levels of cholesterol and triglycerides.
Confezionamento
5 mL Clear Glass Sealed Ampule (810600P-1mg)
Nota sulla preparazione
To prevent aggregation, prepare water-based solutions of 2 mM stock solutions of n-DOXYL PCs and store in plastic. Dilute stock solutions to 0.03- 0.1 mM solutions for EPR studies. For liposome preparations in fluorescent quenching measurements, dissolve the doxyl lipid in 150 μl absolute ethanol for a concentration of 40.3 mM. href="https://pubs.acs.org/doi/suppl/10.1021/ja804929m/suppl_file/ja804929m_si_001.pdf"target="_blank">Supplemental information
Note legali
Avanti Research is a trademark of Avanti Polar Lipids, LLC
Comunemente ordinati con questo prodotto
N° Catalogo
Descrizione
Determinazione del prezzo
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documenti section.
Se ti serve aiuto, non esitare a contattarci Servizio Clienti
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Lipid-specific binding of the calcium-dependent antibiotic daptomycin leads to changes in lipid polymorphism of model membranes
Jung D, et al.
Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 154(2), 120-128 (2008)
The Membranes of Cells, 154(2), 120-128 (2016)
Integrative Medicine - E-Book, 154(2), 120-128 (2017)
Structural insights into the membrane-anchoring mechanism of a cholesterol-dependent cytolysin
Ramachandran R, et al.
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 9(11), 823-823 (2002)
The mechanism of membrane insertion for a cholesterol-dependent cytolysin: a novel paradigm for pore-forming toxins
Shatursky O, et al.
Cell, 99(3), 293-299 (1999)
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.