W365601
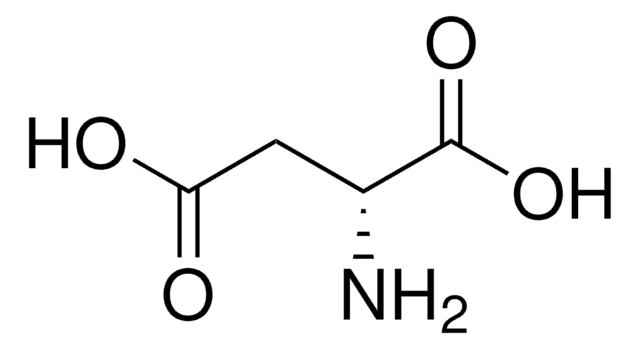
L-Aspartic acid
≥98%, FG
Sinonimo/i:
(S)-(+)-Aminosuccinic acid, (S)-Aminobutanedioic acid
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
synthetic
Livello qualitativo
Grado
FG
agenzia
meets purity specifications of JECFA
Conformità normativa
EU Regulation 1334/2008 & 872/2012
FDA 21 CFR 172.320
Saggio
≥98%
Attività ottica
[α]/D 24.0 to 26.0°, c = 8 in hydrochloric acid (6 N HCl)
Punto di fusione
>300 °C (dec.) (lit.)
applicazioni
flavors and fragrances
Documentazione
see Safety & Documentation for available documents
Allergene alimentare
no known allergens
Organolettico
odorless
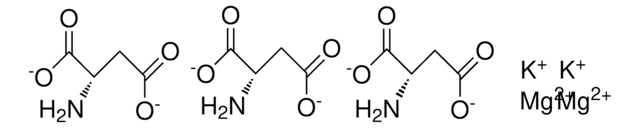
Stringa SMILE
N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H7NO4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m0/s1
CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.