764779
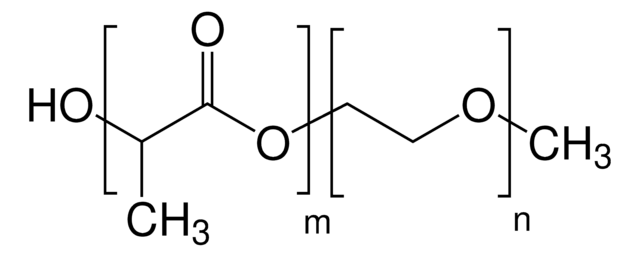
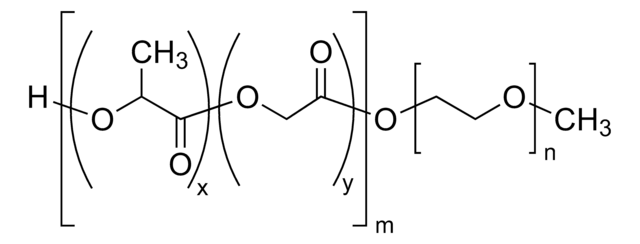
Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether-block-poly(D,L lactide)
PEG average Mn 2,000, PDLLA average Mn 2,000
Sinonimo/i:
PEG-PDLLA
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Descrizione
n=45, m=28 (typical)
typical PEG PDI<1.1; overall PDI<1.4 (THF, PEO)
Livello qualitativo
Forma fisica
pellets
PM
PDLLA average Mn 2,000
PEG average Mn 2,000
average Mn 4,000 (total)
Tempo di degradazione
2-4 weeks
Temp. transizione
Tg 11 °C (PEG block)
Tm 244-248 °C
Tg 88 °C (PDLLA block)
Ind. polidispersione
≤1.4
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
- Good biocompatibility, low immunogenicity and good degradability.
- Properties can be easily modulated by changing the block copolymer segment sizes to suit a particular application.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Local delivery of bioactive molecules using an implantable device can decrease the amount of drug dose required as well as non-target site toxicities compared to oral or systemic drug administration.
Microparticle drug delivery systems have been extensively researched and applied to a wide variety of pharmaceutical and medical applications due to a number of advantages including injectability, local applicability to target tissues and sites, and controlled drug delivery over a given time period.
Aliphatic polyesters such as polylactide, poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and polycaprolactone, as well as their copolymers, represent a diverse family of synthetic biodegradable polymers that have been widely explored for medical uses and are commercially available.
The development of drugs that target specific locations within the human body remains one of the greatest challenges in biomedicine today.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.