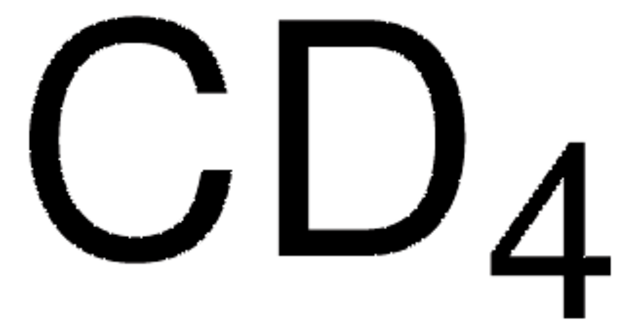490210
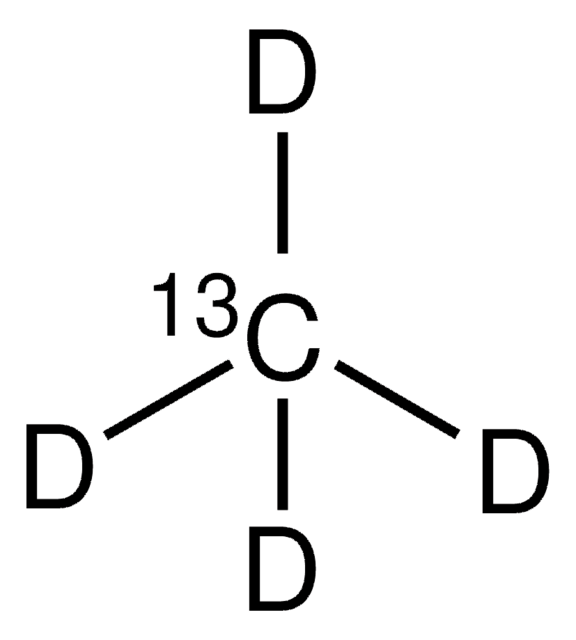
Methane-12C, 13C-depleted
99.9 atom % 12C
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Formula condensata:
12CH4
Numero CAS:
Peso molecolare:
16.03
Numero CE:
Numero MDL:
Codice UNSPSC:
41116107
ID PubChem:
Prodotti consigliati
Descrizione
13C-depleted
Purezza isotopica
99.9 atom % 12C
Spostamento di massa
depleted
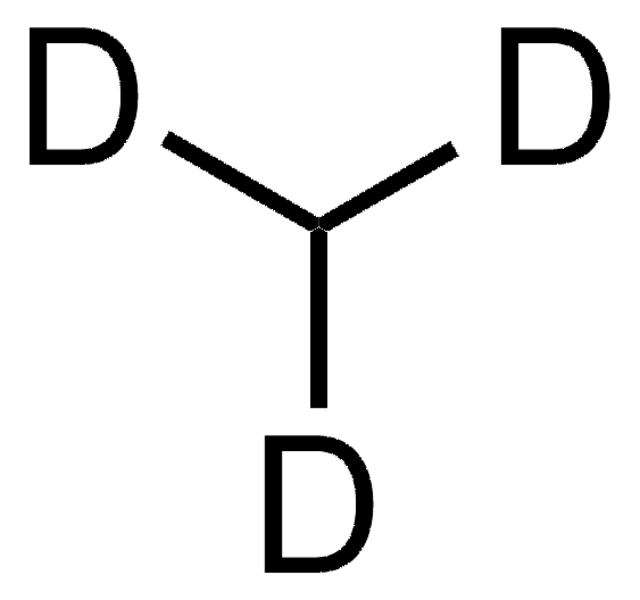
Stringa SMILE
[12CH4]
InChI
1S/CH4/h1H4
VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Categorie correlate
Confezionamento
This product may be available from bulk stock and can be packaged on demand. For information on pricing, availability and packaging, please contact Stable Isotopes Customer Service.
Prodotti consigliati
The use of a brass regulator is recommended.
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Flam. Gas 1A - Press. Gas Compr. Gas
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
2A - Gases
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
nwg
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
-306.4 °F - closed cup
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
-188 °C - closed cup
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Antoine P Pagé et al.
PloS one, 10(7), e0132062-e0132062 (2015-07-15)
The objectives of this study were to uncover Salix purpurea-microbe xenobiotic degradation systems that could be harnessed in rhizoremediation, and to identify microorganisms that are likely involved in these partnerships. To do so, we tested S. purpurea's ability to stimulate
Catharina Vendl et al.
The Journal of experimental biology, 218(Pt 21), 3425-3434 (2015-11-06)
Fundamental differences in methane (CH4) production between macropods (kangaroos) and ruminants have been suggested and linked to differences in the composition of the forestomach microbiome. Using six western grey kangaroos (Macropus fuliginosus) and four red kangaroos (Macropus rufus), we measured
Svenja T Lohner et al.
The ISME journal, 8(8), 1673-1681 (2014-05-23)
Direct, shuttle-free uptake of extracellular, cathode-derived electrons has been postulated as a novel mechanism of electron metabolism in some prokaryotes that may also be involved in syntrophic electron transport between two microorganisms. Experimental proof for direct uptake of cathodic electrons
Wojciech Filipiak et al.
Journal of breath research, 9(1), 016004-016004 (2015-01-06)
Existing methods for the early detection of infections in mechanically ventilated (MV) patients at intensive care units (ICUs) are unsatisfactory. Here we present an exploratory study assessing the feasibility of breath VOC analyses for the non-invasive detection of pathogens in
Garvin A Heath et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111(31), E3167-E3176 (2014-07-23)
Recent technological advances in the recovery of unconventional natural gas, particularly shale gas, have served to dramatically increase domestic production and reserve estimates for the United States and internationally. This trend has led to lowered prices and increased scrutiny on
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.