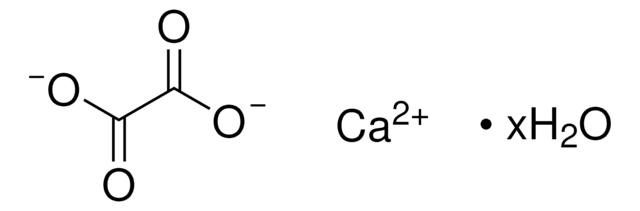455997
Calcium oxalate
≥99.9% trace metals basis
Sinonimo/i:
Calcium oxalate (1:1)
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Formula condensata:
CaC2O4
Numero CAS:
Peso molecolare:
128.10
Numero CE:
Numero MDL:
Codice UNSPSC:
12352302
ID PubChem:
Prodotti consigliati
Grado
for analytical purposes
Saggio
≥99.9% trace metals basis
Stato
powder and chunks
Impurezze
≤1000 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
Densità
2.2 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
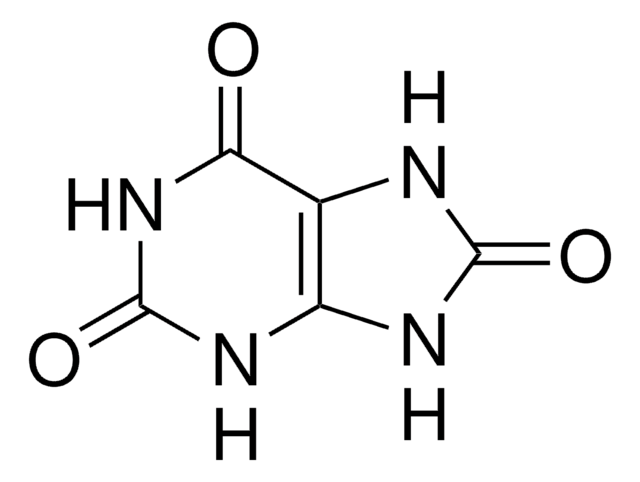
Stringa SMILE
O=C1O[Ca]OC1=O
InChI
1S/C2H2O4.Ca/c3-1(4)2(5)6;/h(H,3,4)(H,5,6);/q;+2/p-2
QXDMQSPYEZFLGF-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Descrizione generale
Calcium oxalate (CaC2O4) belongs to the class of oxalates that are associated with soils and lead litter. It forms crystals that are free-living, pathogenic, and plant symbiotic fungi. It is formed by the re-precipitation of calcium as the oxalate.
Purity based on trace metal analysis
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Atsushi Okada et al.
Clinical and experimental nephrology, 23(5), 710-716 (2019-01-20)
Risk assessment for urinary stones has been mainly based on urinary biochemistry. We attempted to identify the risk factors for urinary stones by statistically analyzing urinary biochemical and inflammation-related factors. Male participants (age, 20-79 years) who visited Nagoya City University Hospital
Jorge M C Mondego et al.
BMC genomics, 9, 548-548 (2008-11-21)
The basidiomycete fungus Moniliophthora perniciosa is the causal agent of Witches' Broom Disease (WBD) in cacao (Theobroma cacao). It is a hemibiotrophic pathogen that colonizes the apoplast of cacao's meristematic tissues as a biotrophic pathogen, switching to a saprotrophic lifestyle
Saeed R Khan
The Journal of urology, 189(3), 803-811 (2012-10-02)
Idiopathic calcium oxalate kidney stones form while attached to Randall plaques, the subepithelial deposits on renal papillary surfaces. Plaque formation and growth mechanisms are poorly understood. Plaque formation elsewhere in the body is triggered by reactive oxygen species and oxidative
James J De Yoreo et al.
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology, 291(6), F1123-F1131 (2006-11-04)
Calcium oxalate monohydrate (COM) is the primary constituent of the majority of renal stones. Osteopontin (OPN), an aspartic acid-rich urinary protein, and citrate, a much smaller molecule, are potent inhibitors of COM crystallization at levels present in normal urine. Current
Baishnisha Amanulla et al.
Scientific reports, 7(1), 14182-14182 (2017-10-29)
Excess nitrite (NO
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.