440175
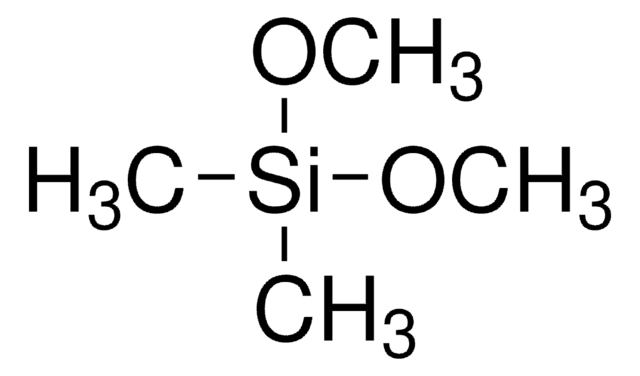
Trimethoxymethylsilane
95%
Sinonimo/i:
MTMS, Methyltrimethoxysilane
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Formula condensata:
CH3Si(OCH3)3
Numero CAS:
Peso molecolare:
136.22
Beilstein:
1736151
Numero CE:
Numero MDL:
Codice UNSPSC:
12352103
ID PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.22
Prodotti consigliati
Saggio
95%
Forma fisica
liquid
Impurezze
3% methyl alcohol
Indice di rifrazione
n20/D 1.371 (lit.)
P. eboll.
102-104 °C (lit.)
Densità
0.955 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Stringa SMILE
CO[Si](C)(OC)OC
InChI
1S/C4H12O3Si/c1-5-8(4,6-2)7-3/h1-4H3
BFXIKLCIZHOAAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Categorie correlate
Applicazioni
Trimethoxymethylsilane (MTMS) is one of the key precursor for the synthesis of:
- Monolithic silica columns with various skeleton sizes for capillary liquid chromatography.
- Ionogels, where an ionic liquid is confined within silica-derived networks.
- Monolithic silica aerogels via acid-base sol-gel polymerization.
- Hydrophobic, flexible, and ultralightweight silylated nanocellulose sponges for the selective removal of oil from water.
Avvertenze
Danger
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Flam. Liq. 2
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
3 - Flammable liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
48.2 °F
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
9 °C
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Methyltrimethoxysilane based monolithic silica aerogels via ambient pressure drying.
Bhagat S D, et al.
Microporous and Mesoporous Materials : The Official Journal of the International Zeolite Association, 100(1-3), 350-355 (2007)
Ultralightweight and flexible silylated nanocellulose sponges for the selective removal of oil from water.
Zhang Z, et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 26(8), 2659-2668 (2014)
Monolithic silica columns with various skeleton sizes and through-pore sizes for capillary liquid chromatography.
Motokawa M, et al.
Journal of Chromatography A, 961(1), 53-63 (2002)
Ionogels, new materials arising from the confinement of ionic liquids within silica-derived networks.
Neouze M A, et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 18(17), 3931-3936 (2006)
Mary E Robbins et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 125(20), 6068-6069 (2003-06-06)
The release of nitric oxide (NO) from polymers has proven to be highly effective at inhibiting platelet adhesion and thus enhancing the blood compatibility of medical implants. Micropatterning techniques were used to design surfaces that release NO while preserving the
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.