224715
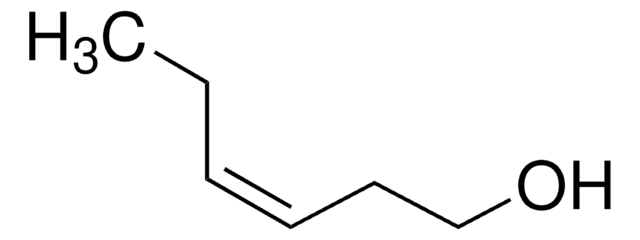
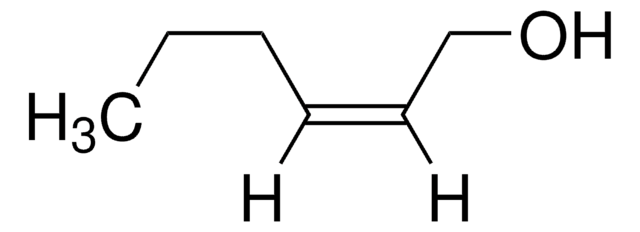
trans-3-Hexen-1-ol
97%
Sinonimo/i:
trans-3-Hexenol
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
97%
Indice di rifrazione
n20/D 1.439 (lit.)
P. ebollizione
61-62 °C/12 mmHg (lit.)
Densità
0.817 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Gruppo funzionale
hydroxyl
Stringa SMILE
[H]\C(CC)=C(\[H])CCO
InChI
1S/C6H12O/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7/h3-4,7H,2,5-6H2,1H3/b4-3+
UFLHIIWVXFIJGU-ONEGZZNKSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Categorie correlate
Descrizione generale
Avvertenze
Warning
Indicazioni di pericolo
Consigli di prudenza
Classi di pericolo
Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 3
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
3 - Flammable liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
138.2 °F - closed cup
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
59 °C - closed cup
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.