推荐产品
生物源
human erythrocytes
品質等級
化驗
>80% protein (biuret)
形狀
essentially salt-free, lyophilized powder
比活性
≥2,500 units/mg protein
分子量
32.0 kDa
成份
Protein, ≥80% biuret
製造商/商標名
Sigma-Aldrich
技術
activity assay: suitable
顏色
white to off-white
pH值範圍
7.6—10.5
pH值
7.8
適合性
suitable for molecular biology
應用
life science and biopharma
儲存溫度
−20°C
基因資訊
human ... SOD1(6647) , SOD2(6648) , SOD3(6649)
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
一般說明
應用
- 在铜绿假单胞菌感染的活性氧 (ROS) 测量研究中检测其对人中性粒细胞的影响
- 作为抗氧化剂,通过光谱法检测其对红细胞 (RBC) 匀浆中大气压等离子体射流 (APPJ) 诱导的活性氧生成的影响
- 检测其对人微血管内皮细胞(HMEC-1)血红蛋白 (Hb) 诱导性核因子-kappa B(NF- κB) 和缺氧诱导因子 (HIF) 活性的削弱作用
- 作为参考抗氧化蛋白,在膳食类黄酮
- 结合过氧化氢酶治疗促进体外细胞分化后,研究其在人肠道 Caco-2 细胞中的表达情况
生化/生理作用
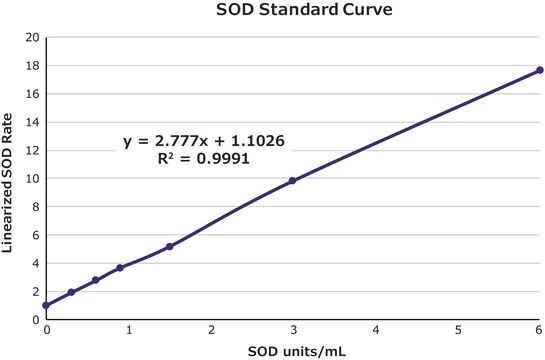
單位定義
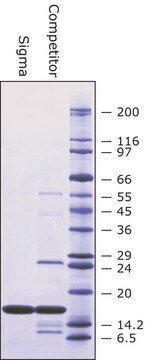
分析報告
訊號詞
Danger
危險聲明
危險分類
Resp. Sens. 1
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
其他客户在看
商品
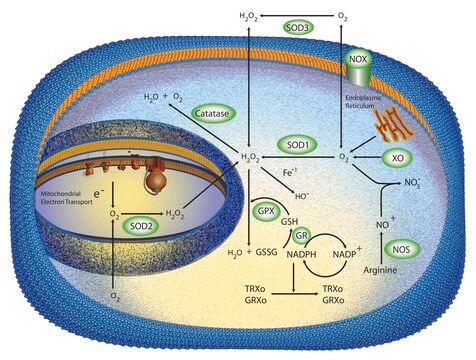
Oxidative stress is mediated, in part, by reactive oxygen species produced by multiple cellular processes and controlled by cellular antioxidant mechanisms such as enzymatic scavengers or antioxidant modulators. Free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species, cause cellular damage via cellular.
实验方案
Enzymatic Assay of Superoxide Dismutase
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门