推荐产品
生物源
mouse
品質等級
共軛
unconjugated
抗體表格
purified from hybridoma cell culture
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
RMdO20, monoclonal
形狀
buffered aqueous solution
物種活性
mouse, rat, human
濃度
~2 mg/mL
技術
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
microarray: suitable
western blot: 1-2 μg/mL using extracts of rat brain S1 fraction.
同型
IgG1
UniProt登錄號
運輸包裝
dry ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... NEFH(4744) , NEFM(4741)
mouse ... Nefh(380684) , Nefm(18040)
rat ... Nefh(24587) , Nefm(24588)
一般說明
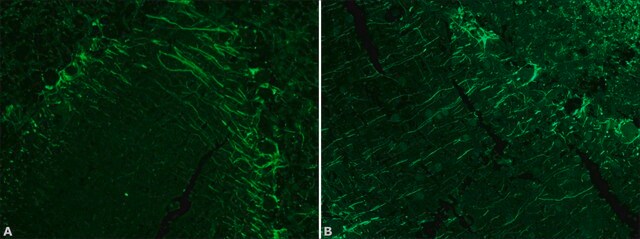
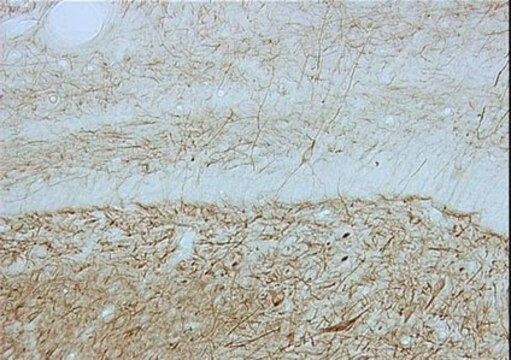
神经丝直径为10 nm,属于中间丝蛋白家族。 神经丝主要在神经元起源的细胞或组织中表达,对于轴突的适当径向生长至关重要。抗神经丝 160/200 单克隆抗体可用于 ELISA 和免疫印迹。它还可以用于微阵列。小鼠抗神经丝 160/200 抗体与小鼠、大鼠和人体内非磷酸化形式的 NF-M 和 NF-H(NF-M/H,约 160 和 200 kDa)发生特异性反应。
免疫原
纯化的中等大小大鼠神经丝 (NF-M) 亚基。
應用
单克隆抗神经丝160/200抗体可用于免疫细胞化学(1:100稀释)和蛋白质印迹(1:1,000稀释)。它还可用于免疫组织化学。
外觀
0.01M 磷酸缓冲盐溶液,pH 7.4,含 15mM 叠氮化钠。
免責聲明
除非我们的产品目录或产品附带的其他公司文档另有说明,否则我们的产品仅供研究使用,不得用于任何其他目的,包括但不限于未经授权的商业用途、体外诊断用途、离体或体内治疗用途或任何类型的消费或应用于人类或动物。
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
其他客户在看
W Yu et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 20(15), 5782-5791 (2000-07-26)
Dendrites are short stout tapering processes that are rich in ribosomes and Golgi elements, whereas axons are long thin processes of uniform diameter that are deficient in these organelles. It has been hypothesized that the unique morphological and compositional features
M K Lee et al.
Current opinion in cell biology, 6(1), 34-40 (1994-02-01)
Neurofilaments make up the major intermediate filament system in mature neurons. Recent studies demonstrate that neurofilaments in vivo are obligate heteropolymers and are required for proper radial growth of axons. Furthermore, forced over-expression of neurofilament subunits in transgenic mice shows
Mariangela Iovino et al.
Brain : a journal of neurology, 138(Pt 11), 3345-3359 (2015-07-30)
Tauopathies, such as Alzheimer's disease, some cases of frontotemporal dementia, corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy, are characterized by aggregates of the microtubule-associated protein tau, which are linked to neuronal death and disease development and can be caused by mutations
Katherine J D A Excoffon et al.
Hearing research, 215(1-2), 1-9 (2006-05-09)
The Coxsackievirus and Adenovirus Receptor (CAR) is an essential regulator of cell growth and adhesion during development. The gene for CAR, CXADR, is located within the genomic locus for Usher syndrome type 1E (USH1E). Based on this and a physical
L Yao et al.
Gene therapy, 20(12), 1149-1157 (2013-07-26)
Functionalized biomaterial scaffolds targeted at improving axonal regeneration by enhancing guided axonal growth provide a promising approach for the repair of spinal cord injury. Collagen neural conduits provide structural guidance for neural tissue regeneration, and in this study it is
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门