推荐产品
生物源
Serratia marcescens
品質等級
重組細胞
expressed in E. coli
化驗
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
形狀
buffered aqueous glycerol solution
分子量
30 kDa
濃度
≥250 units/μL
應用
research use
異物活動
protease, essentially free
運輸包裝
wet ice
儲存溫度
−20°C
正在寻找类似产品? 访问 产品对比指南
一般說明
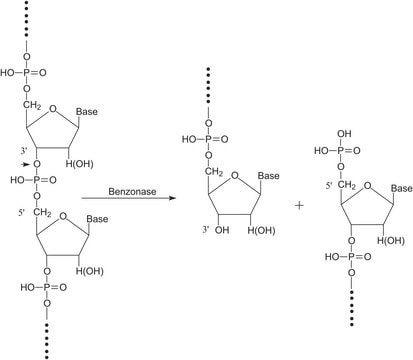
Benzonase®全能核酸酶是一种通过高效基因工程法从粘质沙雷氏菌(Serratia marcescens)中获得的核酸内切酶。这种由两个必需二硫键连接的二聚体蛋白可在宽泛的操作条件下攻击并降解所有形式的DNA和RNA(单链、双链、线性和环化)。Benzonase®全能核酸酶能够去除核酸并提高蛋白质样本的纯度和质量。
應用
Benzonase®全能核酸酶用于:作为冰冷裂解缓冲液C的组分以消化DNA 和 RNA,便于充分释放所有核蛋白在免疫沉淀中用于释放核质和染色质中的蛋白复合物作为RIPA添加剂,用于分离SHSY5Y细胞进行免疫沉淀在脱细胞方法中用于去除主动脉根部的残留核酸
用于去除蛋白样品中的核酸。
生化/生理作用
Benzonase®全能核酸酶能将核酸完全消化成长度为3到5个碱基的5′-单磷酸末端寡核苷酸,使其成为从重组蛋白中去除核酸的理想工具,并适于需要完全消化核酸的应用。除了降低蛋白质提取物的粘度并防止细胞结团之外,使用Benzonase®全能核酸酶预处理蛋白质样本可以消除任何结合的核酸,进而显著提高2D凝胶电泳的分辨率。这种多功能酶可消化天然或热变性的DNA和RNA,其酶活性的最佳pH值为8.0-9.2。Benzonase®全能核酸酶可有效去除微生物组样本中的宿主DNA。在许多情况下,微生物组样本(如唾液或皮肤等)中含有较高比例的能够干扰下游结果的宿主DNA。我们的专家表示,减少宿主DNA可以降低测序成本,同时增加并改进数据。实验数据显示于以下技术文章中-用于微生物组工作流程的Benzonase®全能核酸酶物
消化天然或热变性的DNA和RNA。
特點和優勢
- 去除微生物组样本的宿主DNA。
- 在各种工作流程中高效去除核酸。
- 在蛋白提取过程中降低粘度。
單位定義
在pH 8.0,37 °C条件下,一个单位的酶在30分钟内可将超声的鲑鱼精子DNA消化成等同于1.0 ΔA260的酸可溶寡核苷酸(2.625 ml反应体积)。
外觀
在含有20 mM Tris HCl, pH 8.0, 2 mM MgCl2及20 mM NaCl的50%甘油中的溶液。
其他說明
法律資訊
Benzonase®核酸酶由德国达姆施塔特默克公司和/或其附属公司提供。
Benzonase is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
儲存類別代碼
10 - Combustible liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
個人防護裝備
Eyeshields, Gloves
其他客户在看
Jos J M Drabbels et al.
Blood, 118(19), e149-e155 (2011-09-21)
Microchimerism is defined by the presence of low levels of nonhost cells in a person. We developed a reliable method for separating viable microchimeric cells from the host environment. For flow cytometric cell sorting, HLA antigens were targeted with human
Janus S Jakobsen et al.
Science advances, 5(7), eaaw4304-eaaw4304 (2019-07-17)
The key myeloid transcription factor (TF), CEBPA, is frequently mutated in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), but the direct molecular effects of this leukemic driver mutation remain elusive. To investigate CEBPA mutant AML, we performed microscale, in vivo chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing
T K Ball et al.
Gene, 57(2-3), 183-192 (1987-01-01)
We are studying exoproteins of the enteric bacterium Serratia marcescens as a model system for the release of extracellular proteins from the cell. In this work we report the cloning of the gene for a secreted nuclease from S. marcescens
T K Ball et al.
Nucleic acids research, 20(19), 4971-4974 (1992-10-11)
The role of the two disulfide bonds found in the Serratia marcescens nuclease were tested by site directed mutagenesis and were found essential for nuclease activity, although slight residual activity remained. The requirement for disulfide bond formation may play a
An extracellular nuclease from Serratia marcescens. II. Specificity of the enzyme.
M Nestle et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 244(19), 5219-5225 (1969-10-10)
商品
This discussion will highlight some of these methodologies, namely, the use of Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) and Protein-AQUA.
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门