推荐产品
應用
分散酶I已被用于肺组织消化和流式染色处理,以及小鼠CD4细胞分离。该酶还被用于消化切割伤口及少量周围皮肤,用于GFP+(绿色荧光蛋白)细胞检测。本研究旨在探讨骨髓间充质干细胞的分化和血管生成对创面愈合的影响。它还被用于在小鼠真皮成纤维细胞分离过程中去除表皮。
适用于制备测序用单细胞悬液。
适用于制备测序用单细胞悬液。
分散酶I已被用于评估羊膜在愈合过程早期阶段对伤口大小的影响。 分散酶I还被用于研究以二酪氨酸为底物的蛋白酶测定。
生化/生理作用
分散酶I是一种快速、有效、温和的中性蛋白酶,可以将完整的表皮层与真皮层分开。它还可以将培养物中的完整上皮细胞层与下层分离。该酶可在消化基底膜区域的同时保留上皮细胞的活力。它还可用于防止悬浮培养物中的细胞结块。该蛋白酶可水解纤连蛋白和IV型胶原蛋白,但不能水解层粘连蛋白、V型胶原蛋白、血清白蛋白或转铁蛋白。它可以水解非极性氨基酸残基的N-末端肽键。它优先水解具有暴露疏水氨基酸残基的变性和细胞间蛋白质。Ca2+, Mg2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Fe3+ 和Al3+可以激活该酶活性。EDTA、EGTA、Hg2+ 和其他重金属可抑制该酶活性。每g-mol纯化分散酶I含有1g锌原子。如果通过EDTA或EGTA等螯合剂除去锌成分,则产生无活性的酶蛋白。该酶不受血清抑制。
單位定義
若无其他说明,则一个酶活性单位是指在pH7.5、37℃条件下每分钟水解酪蛋白并产生相当于1.0 μM (181 μg) 酪氨酸的颜色(使用Folin-Ciocalteu试剂显色)所需的酶量。
外觀
冻干粉末,含醋酸钙
法律資訊
Dispase is a registered trademark of Godo Shusei Co., Ltd.
訊號詞
Danger
危險分類
Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
標靶器官
Respiratory system
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
其他客户在看
Yaojiong Wu et al.
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio), 25(10), 2648-2659 (2007-07-07)
Although chronic wounds are common, treatment for these disabling conditions remains limited and largely ineffective. In this study, we examined the benefit of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) in wound healing. Using an excisional wound splinting model, we showed
Alessandra Sacco et al.
Nature, 456(7221), 502-506 (2008-09-23)
Adult muscle satellite cells have a principal role in postnatal skeletal muscle growth and regeneration. Satellite cells reside as quiescent cells underneath the basal lamina that surrounds muscle fibres and respond to damage by giving rise to transient amplifying cells
Alizée Vercauteren Drubbel et al.
Cell stem cell, 28(8), 1411-1427 (2021-04-22)
Columnar metaplasia of the esophagus is the main risk factor for esophageal adenocarcinoma. There is a lack of evidence to demonstrate that esophageal progenitors can be the source of columnar metaplasia. In this study, using transgenic mouse models, lineage tracing
W Zhang et al.
Eye (London, England), 26(6), 872-881 (2012-03-31)
Proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR) is the leading cause of failure of surgery for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Although indirect evidence suggests that this disease might be autoimmune in nature, direct proof for this hypothesis is lacking. The purpose of this study was
Liwen Chen et al.
PloS one, 4(9), e7119-e7119 (2009-09-23)
Studies have shown that allogeneic (allo-) bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) may enhance tissue repair/regeneration. However, recent studies suggest that immune rejection may occur to allo-MSCs leading to reduced engraftment. In this study, we compared allo-BM-MSCs with syngeneic
商品
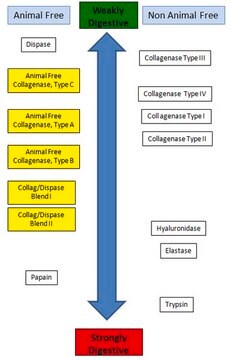
Enzyme Explorer Key Resource: Collagenase Guide.Collagenases, enzymes that break down the native collagen that holds animal tissues together, are made by a variety of microorganisms and by many different animal cells.
Enzyme Explorer关键资源:胶原酶指南。胶原酶是一种可分解将动物组织结合在一起的天然胶原的酶,由多种微生物和不同的动物细胞产生。
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门