推荐产品
生物源
guinea pig
品質等級
抗體表格
affinity isolated antibody
抗體產品種類
primary antibodies
無性繁殖
polyclonal
純化經由
affinity chromatography
物種活性
human, rat, mouse
技術
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable (paraffin)
western blot: suitable
運輸包裝
wet ice
目標翻譯後修改
unmodified
基因資訊
human ... RBFOX3(146713)
mouse ... Rbfox3(52897)
rat ... Rbfox3(287847)
一般說明
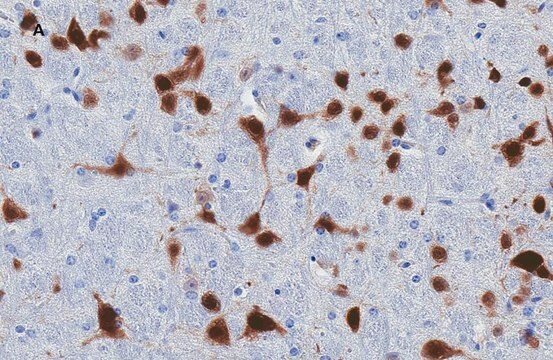
ABN90P是抗NeuN,克隆A60(MAB377)的豚鼠多克隆版本,是高度表征和引用的小鼠单克隆抗体,可特异性识别DNA结合的神经元特异性蛋白NeuN,该蛋白存在于测试的全部脊椎动物的大多数CNS和PNS神经元细胞类型中。NeuN蛋白的分布明显局限于胎儿和成人大脑中的神经元细胞核、核周体和一些近端神经元突起,但有些神经元在所有年龄段都不能被NeuN识别:INL视网膜细胞,Cajal-Retzius细胞,Purkinje细胞,下橄榄和齿状核神经元以及交感神经节细胞就是一些例子。免疫组化检测的NeuN蛋白首先出现在神经元从细胞周期中退出和/或与神经元终末分化开始所对应的发育时间点。免疫反应性出现在小鼠神经管中的E9.5附近,广泛存在于发育中的神经系统中。强烈的核染色表示核调节蛋白功能。从纯化的细胞核中分离出的蛋白质与免疫印迹上的全脑提取物之间没有差异。
特異性
该抗体识别NeuN的N末端。
免疫原
GST标记的重组蛋白,对应于小鼠NeuN的N末端。
表位:N末端
應用
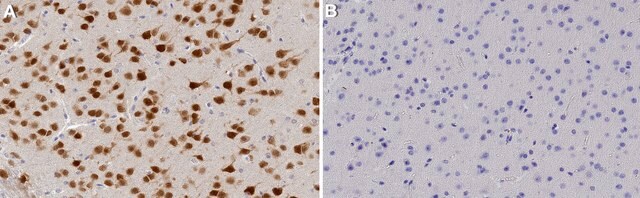
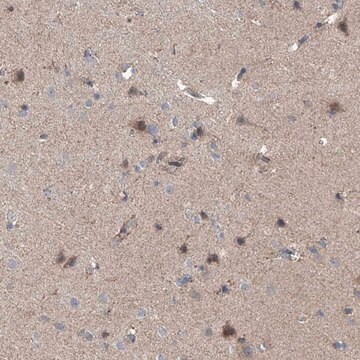
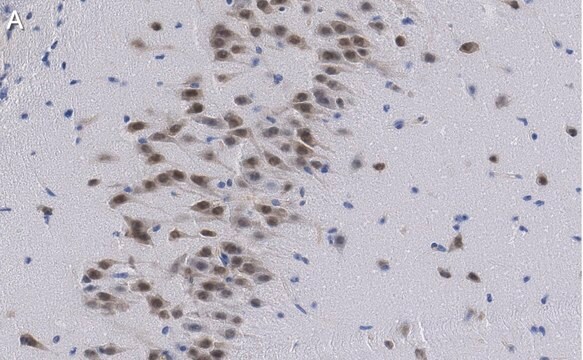
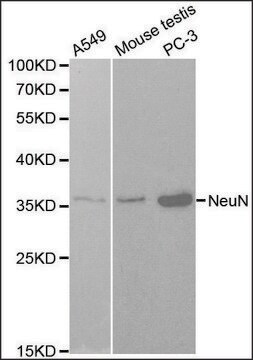
免疫组化分析: 代表性批次的1:1,000稀释液在小鼠额叶皮质组织中检测到NeuN。
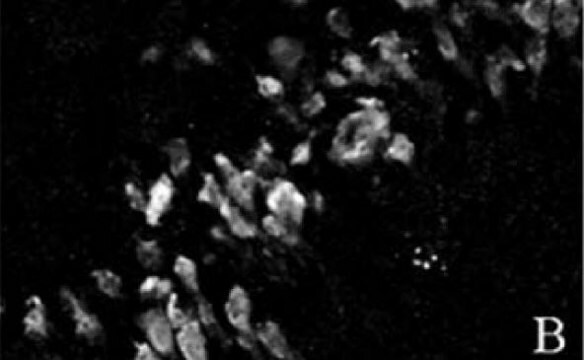
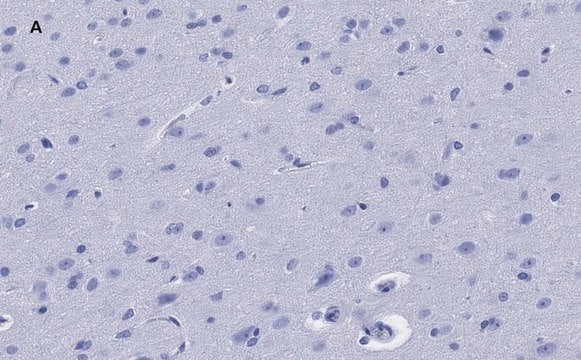
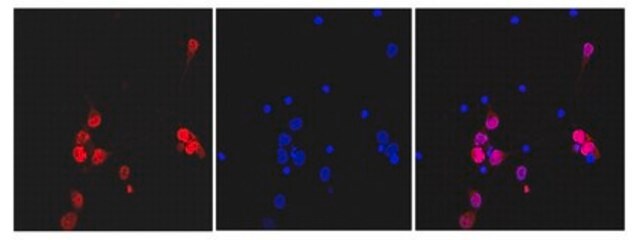
免疫细胞化学分析: 代表性批次的1:1,000-2,000稀释液在大鼠E18皮质细胞中检测到NeuN。
免疫细胞化学分析: 代表性批次的1:1,000-2,000稀释液在大鼠E18皮质细胞中检测到NeuN。
研究子类别
神经 & 胶质标记
神经 & 胶质标记
研究类别
神经科学
神经科学
经验证,该抗NeuN纯化抗体可用于蛋白质印迹、ICC、IHC(P)检测纯化NeuN。
品質
通过蛋白质印迹在小鼠E16脑组织裂解物中进行了评估。
蛋白质印迹分析:该抗体的1:1,000的稀释液在10 µg小鼠E16脑组织裂解物中检测到NeuN。
蛋白质印迹分析:该抗体的1:1,000的稀释液在10 µg小鼠E16脑组织裂解物中检测到NeuN。
標靶描述
观察值〜48 kDa
外觀
在含 0.1 M Tris-甘氨酸(pH 7.4),150 mM NaCl和0.05%叠氮化钠的缓冲液中的纯化的豚鼠多克隆抗体。
抗原亲和纯化
儲存和穩定性
自收到之日起,在 2-8°C 条件下可稳定保存1年
分析報告
对照
小鼠E16脑组织裂解物
小鼠E16脑组织裂解物
其他說明
浓度:请参考批次特异性浓缩物的分析证书。
免責聲明
除非我们的产品目录或产品附带的其他公司文档另有说明,否则我们的产品仅供研究使用,不得用于任何其他目的,包括但不限于未经授权的商业用途、体外诊断用途、离体或体内治疗用途或任何类型的消费或应用于人类或动物。
未找到合适的产品?
试试我们的产品选型工具.
儲存類別代碼
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 1
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
其他客户在看
Dianne E Lee et al.
Molecular imaging, 13 (2014-09-25)
The dopaminergic system is especially vulnerable to the effects of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, rendering dopaminergic deficits early surrogate markers of HIV-associated neuropathology. We quantified dopamine D2/3 receptors in young HIV-1 transgenic (Tg) (n = 6) and age-matched control
Loïc J Chareyron et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(50), 14420-14425 (2016-12-03)
A large population of immature neurons is present in the ventromedial portion of the adult primate amygdala, a region that receives substantial direct projections from the hippocampal formation. Here, we show the effects of neonatal (n = 8) and adult
Kirsty Sawicka et al.
eLife, 8 (2019-12-21)
Loss of the RNA binding protein FMRP causes Fragile X Syndrome (FXS), the most common cause of inherited intellectual disability, yet it is unknown how FMRP function varies across brain regions and cell types and how this contributes to disease
William Schreiber-Stainthorp et al.
Nature communications, 12(1), 2855-2855 (2021-05-19)
Ebola virus (EBOV) causes neurological symptoms yet its effects on the central nervous system (CNS) are not well-described. Here, we longitudinally assess the acute effects of EBOV on the brain, using quantitative MR-relaxometry, 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose PET and immunohistochemistry in a monkey
Jun Nishiyama et al.
Neuron, 96(4), 755-768 (2017-10-24)
Precise genome editing via homology-directed repair (HDR) in targeted cells, particularly in vivo, provides an invaluable tool for biomedical research. However, HDR has been considered to be largely restricted to dividing cells, making it challenging to apply the technique in postmitotic
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门