D0567
DIF-3
≥99% (HPLC), solid
Sinónimos:
1-(3-Chloro-2,6-dihydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-1-hexanone, Differentiation-inducing factor 3
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Nivel de calidad
Ensayo
≥99% (HPLC)
Formulario
solid
solubilidad
DMSO: soluble 46 mg/mL
cadena SMILES
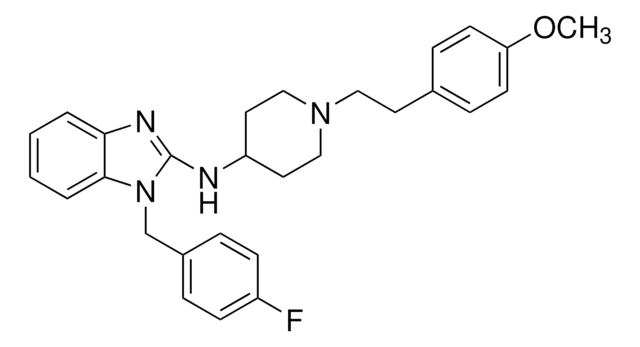
CCCCCC(=O)c1c(O)cc(OC)c(Cl)c1O
InChI
1S/C13H17ClO4/c1-3-4-5-6-8(15)11-9(16)7-10(18-2)12(14)13(11)17/h7,16-17H,3-6H2,1-2H3
Clave InChI
JWBMZIJMSBFBIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Descripción general
Aplicación
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
¿No ve la versión correcta?
Si necesita una versión concreta, puede buscar un certificado específico por el número de lote.
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico