Wichtige Dokumente
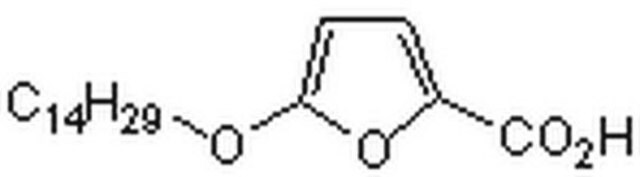
T6575
TOFA
≥98% (HPLC)
Synonym(e):
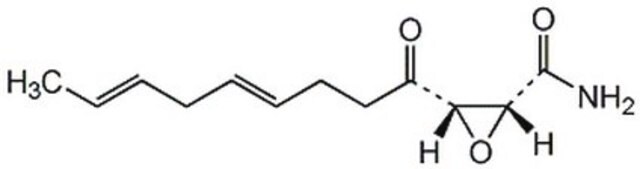
5-(Tetradecyloxy)-2-furoic acid
About This Item
Empfohlene Produkte
Assay
≥98% (HPLC)
Form
powder
Farbe
white to beige
mp (Schmelzpunkt)
112-115 °C
Löslichkeit
DMSO: 2 mg/mL, clear
Lagertemp.
−20°C
SMILES String
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCOc1ccc(o1)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C19H32O4/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-16-22-18-15-14-17(23-18)19(20)21/h14-15H,2-13,16H2,1H3,(H,20,21)
InChIKey
CZRCFAOMWRAFIC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Anwendung
Biochem./physiol. Wirkung
Angaben zur Herstellung
Lagerklassenschlüssel
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flammpunkt (°F)
Not applicable
Flammpunkt (°C)
Not applicable
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Hier finden Sie alle aktuellen Versionen:
Besitzen Sie dieses Produkt bereits?
In der Dokumentenbibliothek finden Sie die Dokumentation zu den Produkten, die Sie kürzlich erworben haben.
Kunden haben sich ebenfalls angesehen
Artikel
Information on fatty acid synthesis and metabolism in cancer cells. Learn how proliferatively active cells require fatty acids for functions such as membrane generation, protein modification, and bioenergetic requirements. These fatty acids are derived either from dietary sources or are synthesized by the cell.
Unser Team von Wissenschaftlern verfügt über Erfahrung in allen Forschungsbereichen einschließlich Life Science, Materialwissenschaften, chemischer Synthese, Chromatographie, Analytik und vielen mehr..
Setzen Sie sich mit dem technischen Dienst in Verbindung.