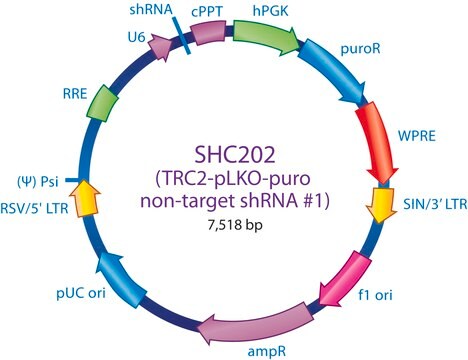
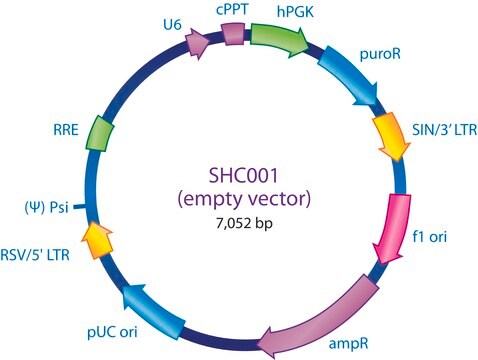
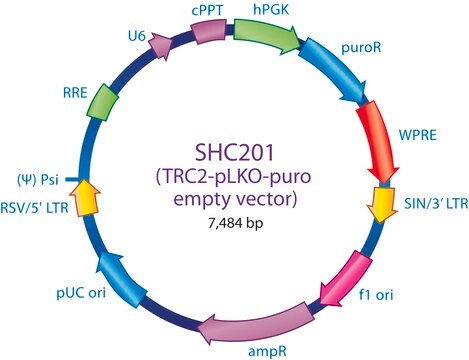
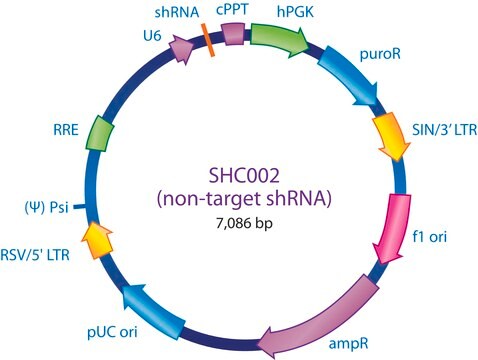
SHC201
MISSION® TRC2 pLKO.5-puro Empty Vector Control Plasmid DNA
Contains no shRNA insert
Sinonimo/i:
MISSION® Control Vectors
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Nome Commerciale
MISSION®
Concentrazione
500 ng/μL in TE buffer; DNA (10μg of plasmid DNA)
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
The MISSION TRC2 Control Vector pLKO-puro is a lentivirus plasmid vector. This vector is in the TRC2 pLKO-puro plasmid backbone, which contains the WPRE. The vector does not contain an shRNA insert and is useful as a negative control in experiments using the TRC2 MISSION shRNA library clones. This allows one to examine the effect of transfection on gene expression and interpret the knockdown effect seen with shRNA clones.
Ampicillin and puromycin antibiotic resistance genes provide selection in bacterial or mammalian cells respectively. In addition, self-inactivating replication incompetent viral particles can be produced in packaging cells (HEK293T) by co-transfection with compatible packaging plasmids (SHP001). The TRC2 pLKO-puro Control Vector is provided as 10 μg of plasmid DNA in Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer at a concentration of 500 ng/μl.
Ampicillin and puromycin antibiotic resistance genes provide selection in bacterial or mammalian cells respectively. In addition, self-inactivating replication incompetent viral particles can be produced in packaging cells (HEK293T) by co-transfection with compatible packaging plasmids (SHP001). The TRC2 pLKO-puro Control Vector is provided as 10 μg of plasmid DNA in Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer at a concentration of 500 ng/μl.
Applicazioni
MISSION® TRC2 pLKO.5-puro Empty Vector Control Plasmid DNA has been used in:
- CRISPR library generation
- Viral constructs
- Plasmid construction
- CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockouts.
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) expressed from short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) are a powerful way to mediate gene specific RNA interference (RNAi) in mammalian cells. The MISSION product line is based on a viral vector-based RNAi library against annotated mouse and human genes. shRNAs that generate siRNAs intracellularly are expressed from amphotropic lentivirus viral particles, allowing screening in a wide range of mammalian cell lines. In these cell lines, MISSION shRNA clones permit rapid, cost efficient loss-of-function and genetic interaction screens.
To see more application data, protocols, vector maps visit sigma.com/shrna.
Note legali
Use of this product is subject to one or more license agreements. For details, please see http://sigmaaldrich.com/missionlicense.
MISSION is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Raccomandato
N° Catalogo
Descrizione
Determinazione del prezzo
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Functional screening implicates miR-371-3p and peroxiredoxin 6 in reversible tolerance to cancer drugs.
Sahu N, et al.
Nature Communications, 7, 12351-12351 (2016)
A CRISPR screen identifies MAPK7 as a target for combination with MEK inhibition in KRAS mutant NSCLC.
Dompe N, et al.
PLoS ONE, 13(6), e0199264-e0199264 (2018)
Silencing of retrotransposons by SETDB1 inhibits the interferon response in acute myeloid leukemia.
Cuellar TL, et al.
The Journal of Cell Biology (2017)
Janet Lau et al.
Nature communications, 8, 14572-14572 (2017-02-22)
Expression of PD-L1, the ligand for T-cell inhibitory receptor PD-1, is one key immunosuppressive mechanism by which cancer avoids eradication by the immune system. Therapeutic use of blocking antibodies to PD-L1 or its receptor PD-1 has produced unparalleled, durable clinical
Dakota L Jones et al.
The Journal of cell biology, 220(5) (2021-02-25)
Matrix stiffness is a central regulator of fibroblast function. However, the transcriptional mechanisms linking matrix stiffness to changes in fibroblast phenotype are incompletely understood. Here, we evaluated the effect of matrix stiffness on genome-wide chromatin accessibility in freshly isolated lung
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.