G1424
Globomycin from Streptomyces hagronensis
Sinonimo/i:
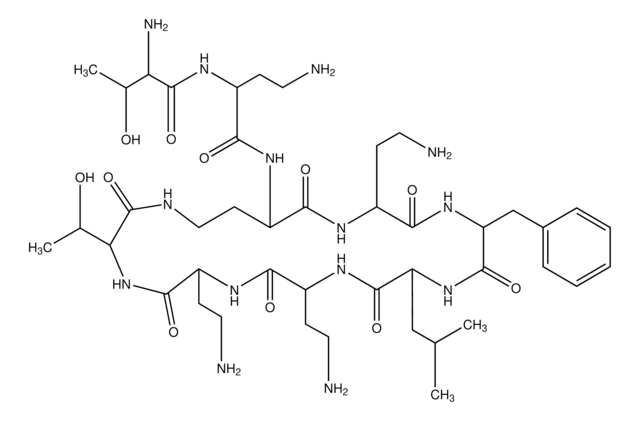
Globomycin, Glycine, N-(N-(N-(N-(N-(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-oxononyl)-N-methylleucyl)-L-alloisoleucyl)-L-seryl)-L-allothreonyl)-, rho-lactone, SF 1902
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
Streptomyces hagronensis
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥98% (HPLC)
Forma fisica
powder
Colore
white
Solubilità
DMSO: 1 mg/mL
Spettro attività antibiotica
Gram-negative bacteria
Modalità d’azione
enzyme | inhibits
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
−20°C
InChI
1S/C32H57N5O9/c1-9-11-12-13-14-24-20(6)32(45)37(8)23(15-18(3)4)29(42)35-26(19(5)10-2)31(44)34-22(17-38)28(41)36-27(21(7)39)30(43)33-16-25(40)46-24/h18-24,26-27,38-39H,9-17H2,1-8H3,(H,33,43)(H,34,44)(H,35,42)(H,36,41)
VFGBXFZXJAWPOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Descrizione generale
Applicazioni
- Globomycin, a new peptide antibiotic with spheroplast-forming activity. I. Taxonomy of producing organisms and fermentation.: This study explores the taxonomy of the producing organisms of Globomycin and details the fermentation processes involved. This antibiotic shows spheroplast-forming activity, indicating its potential application in targeting bacterial cell wall synthesis (Inukai et al., 1978).
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.