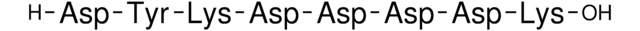CELLMM2
FLAG® M Purification Kit
For Mammalian expression systems.
Sinonimo/i:
Anti-ddddk, Anti-dykddddk
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
tecniche
protein extraction: suitable
Condizioni di spedizione
wet ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Applicazioni
Learn more product details in our FLAG® application portal.
Caratteristiche e vantaggi
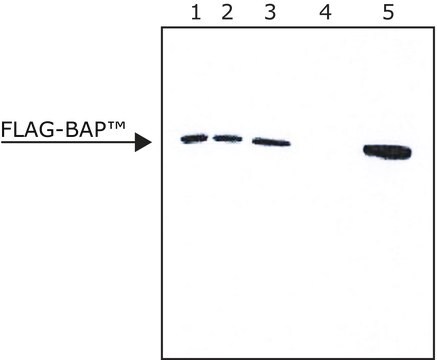
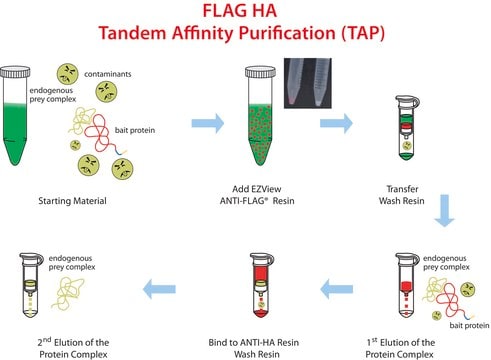
- Includes ready to use reagents, columns, and a detailed protocol for affinity purification of FLAG fusion proteins.
- ANTI-FLAG M2 Affinity Gel allows efficient binding of FLAG fusion proteins without the need for preliminary steps and calibrations.
- Two alternatives for efficient elution conditions (by acidic conditions or by competition with FLAG peptide).
Confezionamento
Altre note
Note legali
I componenti del kit sono disponibili anche separatamente
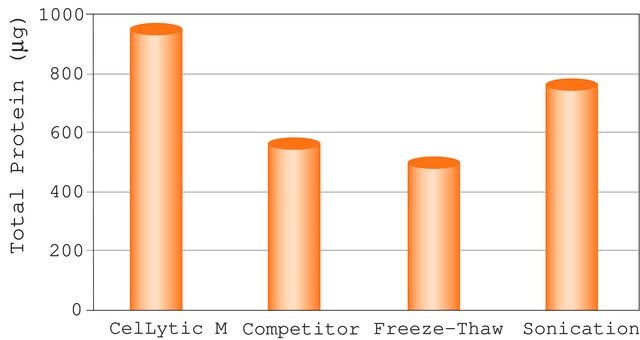
- C2978CelLytic™ M, Cell Lysis Reagent, Suitable for Mammalian cell lysis and protein solubilization.SDS
- SAE0194Purified 3xFLAG® peptide, ≥95% (HPLC), lyophilized powderSDS
- A2220ANTI-FLAG® M2 Affinity Gel, purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous glycerol solutionSDS
- C2103Chromatography columns, general-purpose, volume 10 mL, Overall H 5 in.SDS
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
10 - Combustible liquids
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Contenuto correlato
Protein purification techniques, reagents, and protocols for purifying recombinant proteins using methods including, ion-exchange, size-exclusion, and protein affinity chromatography.
Protein expression technologies for expressing recombinant proteins in E. coli, insect, yeast, and mammalian expression systems for fundamental research and the support of therapeutics and vaccine production.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.