C6706
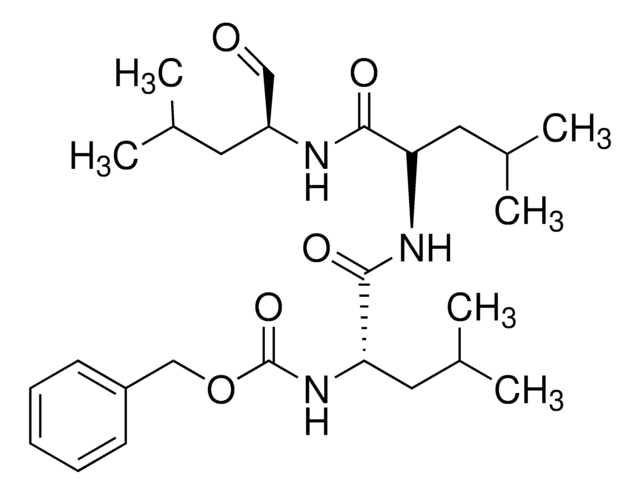
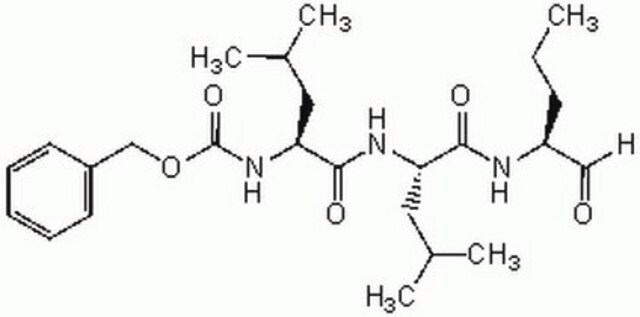
Z-Leu-Leu-Norvalinal
≥90% (HPLC), powder
Sinonimo/i:
MG115, Z-LLnV
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Saggio
≥90% (HPLC)
Forma fisica
powder
Colore
white
Solubilità
DMSO: soluble
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Stringa SMILE
CCC[C@H](NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)OCc1ccccc1)C=O
InChI
1S/C25H39N3O5/c1-6-10-20(15-29)26-23(30)21(13-17(2)3)27-24(31)22(14-18(4)5)28-25(32)33-16-19-11-8-7-9-12-19/h7-9,11-12,15,17-18,20-22H,6,10,13-14,16H2,1-5H3,(H,26,30)(H,27,31)(H,28,32)/t20-,21-,22-/m0/s1
QEJRGURBLQWEOU-FKBYEOEOSA-N
Informazioni sul gene
human ... PSMA1(5682) , PSMC1(5700)
mouse ... PSMA1(26440) , PSMC1(19179)
rat ... PSMA1(29668) , PSMC1(117263)
Amino Acid Sequence
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.