B0753
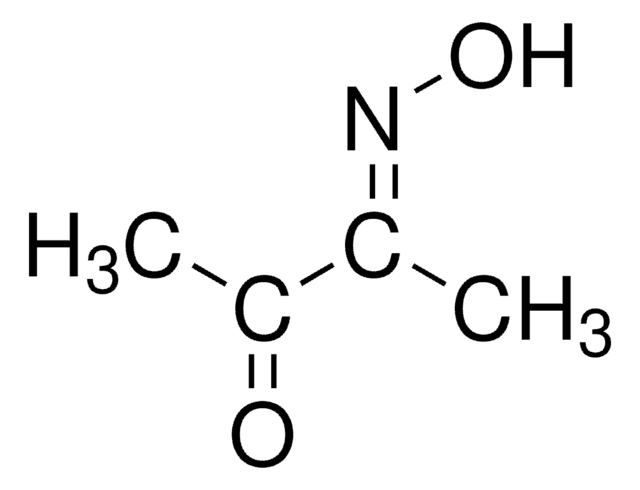
2,3-Butanedione monoxime
≥98% (GC), powder, ATP-sensitive K⁺ and Ca²⁺ channel inhibitor
Sinonimo/i:
BDM
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
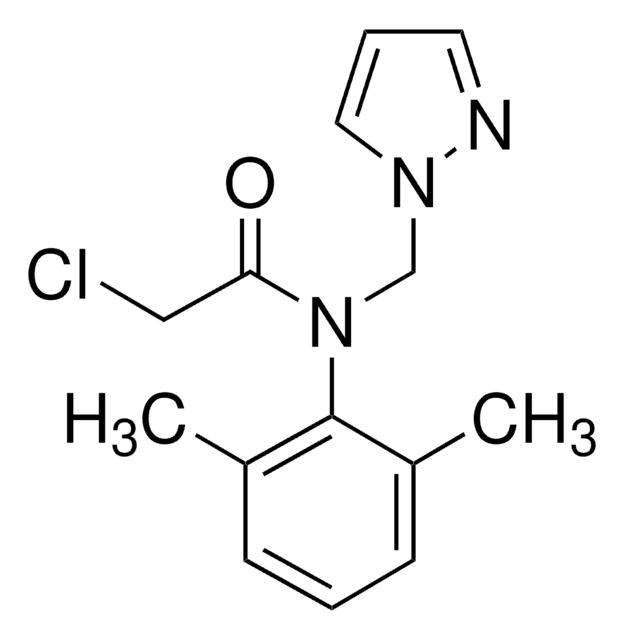
Formula condensata:
CH3C(=NOH)COCH3
Numero CAS:
Peso molecolare:
101.10
Beilstein:
605582
Numero CE:
Numero MDL:
Codice UNSPSC:
12352200
ID PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.77
Prodotti consigliati
Nome del prodotto
2,3-Butanedione monoxime, ≥98%
Saggio
≥98%
Stato
powder
P. ebollizione
185-186 °C (lit.)
Punto di fusione
75-78 °C (lit.)
Stringa SMILE
CC(=O)\C(C)=N\O
InChI
1S/C4H7NO2/c1-3(5-7)4(2)6/h7H,1-2H3/b5-3+
FSEUPUDHEBLWJY-HWKANZROSA-N
Informazioni sul gene
human ... KCNB1(3745)
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Applicazioni
2,3-Butanedione monoxime has been used:
- in single-molecule myosin V motility assays
- as an anesthetic in the approach of imaging transgenic animals
- to reduce rigor tension in muscle fibres
- as a media component for mice cardiomyocytes culture
Azioni biochim/fisiol
2,3-Butanedione monoxime is inhibitor of ATP-sensitive K+ and Ca2+ channels.
DRK1 is a delayed rectifier (Kv2.1) cloned K+ channel from rat brain with consensus sites for protein kinase-dependent phosphorylation that might be expected to be functionally regulated by phosphorylation. 2,3-Butanedione monoxime (BDM) chemically removes phosphate groups from many proteins, and its action on DRK1 channels was examined after expression of DRK1 cRNA in Xenopus oocytes. In two-microelectrode voltage-clamp experiments, the application of 2,3-Butanedione monoxime to the bath inhibited DRK1 current (ki = 16.6 mM, H = 0.96) rapidly and reversibly, with a time course similar to the time course of solution change within the bath. DRK1 current was inhibited at all potentials; the time course of current activation, deactivation and inactivation were unaffected by 2,3-Butanedione monoxime. In inside-out patch-clamp experiments, the application of 2,3-Butanedione monoxime to the cytoplasmic surface similarly inhibited channel activity rapidly and reversibly (ki = 10.7 mM, H = 1.01) in the absence of rephosphorylating substrates. These results are inconsistent with a phosphatase effect, because such an effect should be irreversible in cell-free, ATP-free patches. Instead, the results suggest that 2,3-Butanedione monoxime can inhibit DRK1 channels directly from inside or outside of the membrane.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Dispositivi di protezione individuale
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
M L Riccio et al.
Circulation research, 84(8), 955-963 (1999-05-01)
Despite recent advances in our understanding of the mechanism for ventricular fibrillation (VF), important electrophysiological aspects of the development of VF still are poorly defined. It has been suggested that the onset of VF involves the disintegration of a single
A transgenic approach to live imaging of heparan sulfate modification patterns
Glycosaminoglycans, 253-268 (2015)
Deficiency of mouse mast cell protease 4 mitigates cardiac dysfunctions in mice after myocardium infarction
Wang Yunzhe, et al.
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease (2019)
Venkatakaushik Voleti et al.
Nature methods, 16(10), 1054-1062 (2019-09-29)
The limited per-pixel bandwidth of most microscopy methods requires compromises between field of view, sampling density and imaging speed. This limitation constrains studies involving complex motion or fast cellular signaling, and presents a major bottleneck for high-throughput structural imaging. Here
Tilting and wobble of myosin V by high-speed single-molecule polarized fluorescence microscopy.
Beausang JF et al
Biophysical Journal, 104(6), 1263-1273 (2013)
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.