61909
Atto Rho14 NHS ester
BioReagent, suitable for fluorescence
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Codice UNSPSC:
12352108
NACRES:
NA.32
Prodotti consigliati
Nome Commerciale
BioReagent
Saggio
≥90.0% (HPLC)
Stato
solid
Produttore/marchio commerciale
ATTO-TEC GmbH
Grado di funzionalizzazione
≥90.0%
λ
in ethanol (with 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid)
Assorbanza UV
λ: 624.0-630.0 nm Amax
Compatibilità
suitable for fluorescence
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Applicazioni
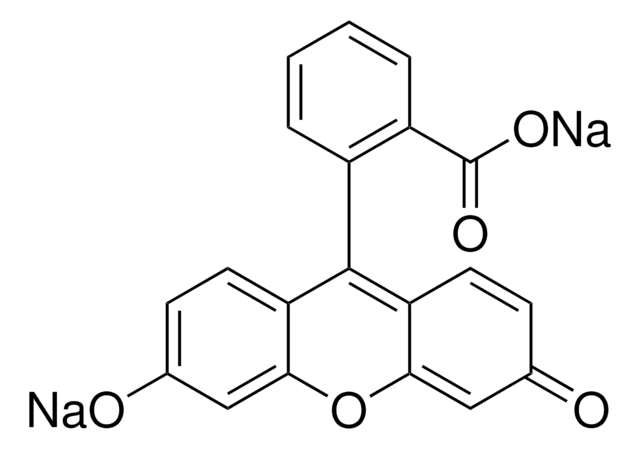
Atto Rho14 NHS ester is a new rhodamine featuring a functionality for coupling to bio-molecules such as DNA, RNA or proteins. The label shows strong absorption and extraordinarily high fluorescence quantum yield. ATTO Rho14 is the brightest label available in this wavelength range. The dye exhibits an exceptionally high photostability. In common with most ATTO-labels, absorption and fluorescence are pH-independent in the range of pH 2 to 11, used in typical applications. The dye is moderately hydrophilic. After coupling to a substrate ATTO Rho14 carries a net electrical charge of +1.
Note legali
This product is for Research use only. In case of intended commercialization, please contact the IP-holder (ATTO-TEC GmbH, Germany) for licensing.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Chao Ma et al.
Analytica chimica acta, 734, 69-78 (2012-06-19)
This article describes the design and preparation of a novel fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based ratiometric sensor with the polymer nanoparticle as scaffold for detecting Hg(2+) in aqueous media. In this study, a fluorescent dye fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC, served as
Yuan-Qiang Sun et al.
Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 51(31), 7634-7636 (2012-06-08)
Probes to dye for: Rhodamine-inspired Si-pyronine, Si-rhodamine, Te-rhodamine, and Changsha NIR dyes have been developed recently. These dyes show fluorescence in the far-red to near-infrared region, while retaining the advantages of the original rhodamines, such as high fluorescence quantum yield
Raphael Alford et al.
Molecular imaging, 8(6), 341-354 (2009-12-17)
Fluorophores are potentially useful for in vivo cancer diagnosis. Using relatively inexpensive and portable equipment, optical imaging with fluorophores permits real-time detection of cancer. However, fluorophores can be toxic and must be investigated before they can be administered safely to
Jianghong Rao et al.
Current opinion in biotechnology, 18(1), 17-25 (2007-01-20)
In vivo fluorescence imaging uses a sensitive camera to detect fluorescence emission from fluorophores in whole-body living small animals. To overcome the photon attenuation in living tissue, fluorophores with long emission at the near-infrared (NIR) region are generally preferred, including
Chunbai He et al.
Biomaterials, 33(33), 8569-8578 (2012-08-22)
Polymeric nanoparticles have been widely applied to oral delivery of protein drugs, however, few studies focused on the systematical elucidation of the size-dependent oral absorption mechanism with well-defined polymeric nanoparticles. Rhodamine B labeled carboxylated chitosan grafted nanoparticles (RhB-CCNP) with different
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.