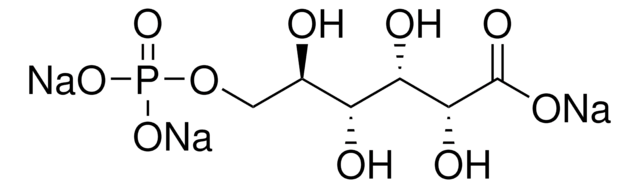
15732
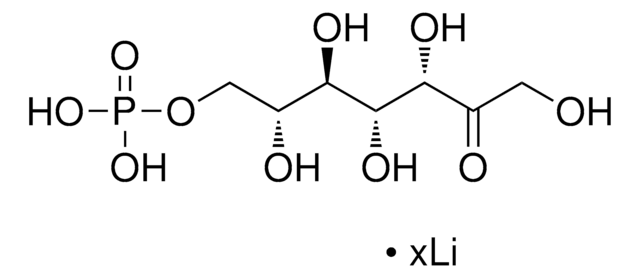
D-Xylulose 5-phosphate lithium salt
≥90% (TLC)
Autenticatiper visualizzare i prezzi riservati alla tua organizzazione & contrattuali
About This Item
Formula empirica (notazione di Hill):
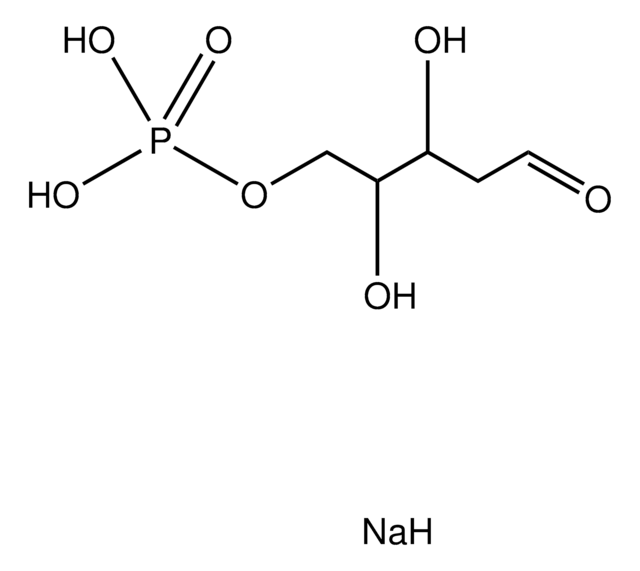
C5H11O8P · xLi+
Numero CAS:
Peso molecolare:
230.11 (free acid basis)
Numero MDL:
Codice UNSPSC:
12352201
ID PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.25
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥90% (TLC)
Stato
powder or crystals
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Stringa SMILE
OCC([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)COP(O)(O)=O)=O
InChI
1S/C5H11O8P/c6-1-3(7)5(9)4(8)2-13-14(10,11)12/h4-6,8-9H,1-2H2,(H2,10,11,12)/t4-,5-/m1/s1
FNZLKVNUWIIPSJ-RFZPGFLSSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Azioni biochim/fisiol
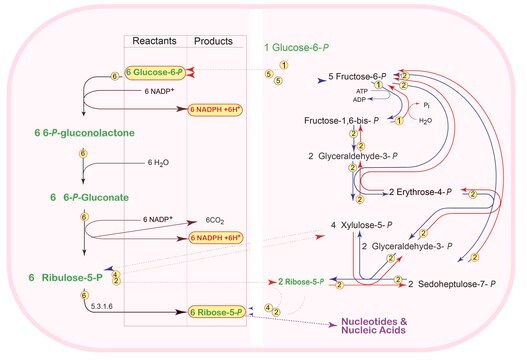
D-Xylulose 5-phosphate (D-Xu-5-P) is a metabolite of the hexose monophosphate pathway activating protein phosphatase 2A to mediate the acute effects of carbohydrate feeding on the glycolytic pathway, the coordinated control of enzymes required in fatty acid & triglyceride synthesis. D-Xylulose 5-phosphate is the signal for the coordinated control of lipogenesis. The elevation of D-Xylulose 5-phosphate is the coordinating signal that both acutely activates phosphofructokinase in glycolysis and promotes the action of the transcription factor ChREBP to increase transcription of the genes for the enzymes of lipogenesis, the hexose monophosphate shunt, and glycolysis, all of which are required for the de novo synthesis of fat.
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
J J Wang et al.
Alcoholism, clinical and experimental research, 21(4), 576-580 (1997-06-01)
Thiamine deficiency, a frequent complication of alcoholism, contributes significantly to the development of damage in various organ systems, including the brain. The molecular mechanisms that underlie the differential vulnerabilities to thiamine deficiency of tissue and cell types and among individuals
Kostas Tsintzas et al.
Clinical science (London, England : 1979), 124(11), 675-684 (2013-01-16)
Physiological hyperglycaemia and hyperinsulinaemia are strong modulators of gene expression, which underpins some of their well-known effects on insulin action and energy metabolism. The aim of the present study was to examine whether acute in vivo exposure of healthy humans
Susen Becker et al.
Journal of chromatography. B, Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences, 883-884, 68-75 (2011-11-15)
The analysis of metabolites in human body fluids remains a challenge because of their chemical diversity and dynamic concentration range. Liquid chromatography (LC) in combination with tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) offers a robust, reliable, and economical methodology for quantitative single
Sigrun Langbein et al.
International journal of cancer, 122(11), 2422-2428 (2008-02-28)
Targeted therapies have demonstrated clinical benefit with limited impact on long-term disease specific survival in the treatment of renal cell cancer (RCC). New opportunities for the treatment of tumors that are resistant or have relapsed, are needed. Increased anaerobic glucose
Diana Hartmannsberger et al.
Cancer letters, 300(1), 20-29 (2010-10-05)
Transketolase-like protein 1 (TKTL1) is a member of the family of transketolase enzymes of which the founder member transketolase (TKT) is known to play a central role in the non-oxidative part of the pentose phosphate pathway. According to several publications
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.