911798
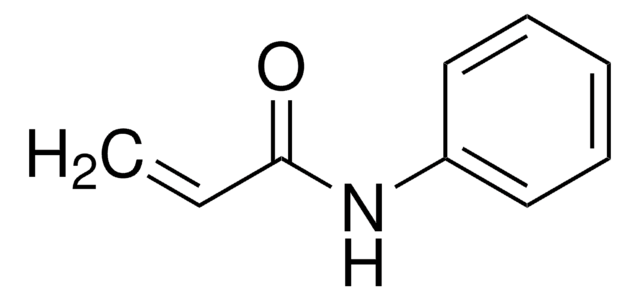
N-(4-Bromophenyl)-N-phenylacrylamide
≥95%
Sinonimo/i:
Electrophilic scout fragment, KB05, Scout fragment for targetable cysteine
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
≥95%
Stato
(Powder or crystals or solid or chunks)
Temperatura di conservazione
2-8°C
Stringa SMILE
Brc1ccc(cc1)N(c2ccccc2)C(=O)C=C
InChI
1S/C15H12BrNO/c1-2-15(18)17(13-6-4-3-5-7-13)14-10-8-12(16)9-11-14/h2-11H,1H2
WFQQVUPOAKOTGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Applicazioni
Altre note
Note legali
Prodotti correlati
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 3
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documenti section.
Se ti serve aiuto, non esitare a contattarci Servizio Clienti
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
Articoli
Ligandability describes the propensity of a protein target to bind a small molecule with high affinity. It is a precursor to evaluating druggability, which requires more advanced translational pharmacological effects and drug-like properties in vivo.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.