725692
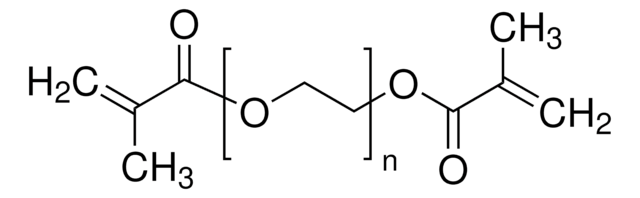
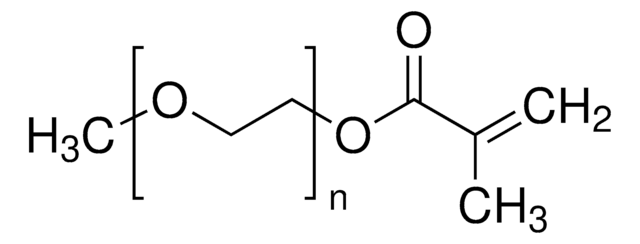
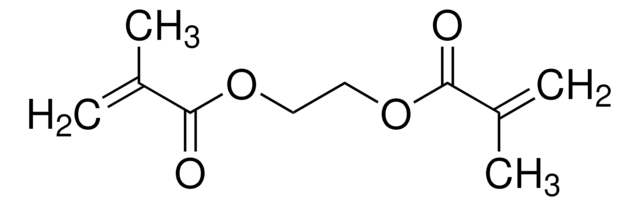
Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate
average MN 20,000, cross-linking reagent polymerization reactions, methacrylate, ≤1, 500 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor (may contain)
Sinonimo/i:
Polyethylene glycol, PEG dimethacrylate
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Nome del prodotto
Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate, average Mn 20,000, contains MEHQ as inhibitor
Stato
powder
PM
average Mn 20,000
contiene
MEHQ as inhibitor
≤1,500 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor (may contain)
Impiego in reazioni chimiche
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
P. ebollizione
>200 °C/2 mmHg (lit.)
Temp. transizione
Tm 59-64 °C
Mw/Mn
≤1.1
Estremità Ω
methacrylate
Estremità α
methacrylate
Architettura del polimero
shape: linear
functionality: homobifunctional
Temperatura di conservazione
−20°C
Stringa SMILE
OCCO.CC(=C)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C10H14O4/c1-7(2)9(11)13-5-6-14-10(12)8(3)4/h1,3,5-6H2,2,4H3
STVZJERGLQHEKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Nota sulla preparazione
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Non trovi la versione di tuo interesse?
Se hai bisogno di una versione specifica, puoi cercare il certificato tramite il numero di lotto.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Patterning of PEG-based Hydrogels - Engineering Spatial Complexity
The use of hydrogel-based biomaterials for the delivery and recruitment of cells to promote tissue regeneration in the body is of growing interest. This article discussed the application of hydrogels in cell delivery and tissue regeneration.
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.