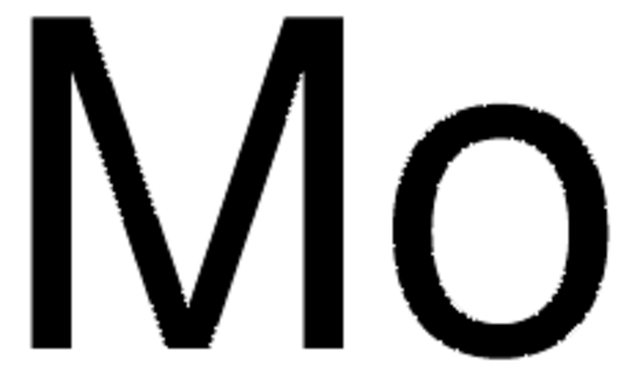266914
Molybdenum
wire, diam. 1.0 mm, 99.95% trace metals basis
Sinonimo/i:
Molybdenum element
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Livello qualitativo
Saggio
99.95% trace metals basis
Stato
wire
Resistività
5.0 μΩ-cm, 20°C
Diametro
1.0 mm
P. ebollizione
4612 °C (lit.)
Punto di fusione
2617 °C (lit.)
Densità
10.3 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Stringa SMILE
[Mo]
InChI
1S/Mo
ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Categorie correlate
Quantità
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
nwg
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Scegli una delle versioni più recenti:
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Articoli
Biomedical implants are essentially foreign substances within the human body that must survive many years’ exposure to demanding mechanical and physiological conditions. Despite these challenges, metal implants have been widely used to substitute for or rebuild hard tissues such as bones and teeth.
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.