E6383
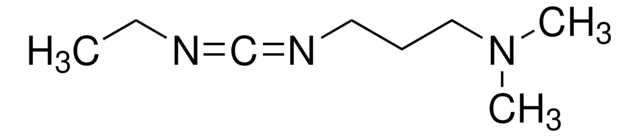
N-(3-Diméthylaminopropyl)-N′-éthylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
crystalline
Synonyme(s) :
N-Éthyl-N′-(3-diméthylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride, EDAC, EDC, EDC hydrochloride, WSC hydrochloride
About This Item
Produits recommandés
product name
N-(3-Diméthylaminopropyl)-N′-éthylcarbodiimide hydrochloride, crystalline
Forme
crystalline
Niveau de qualité
Pertinence de la réaction
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reaction type: Peptide Synthesis
Couleur
white to off-white
Pf
110-115 °C (lit.)
Solubilité
H2O: ≤100 mg/mL
Application(s)
advanced drug delivery
general analytical
Température de stockage
−20°C
Chaîne SMILES
Cl.CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C
InChI
1S/C8H17N3.ClH/c1-4-9-8-10-6-5-7-11(2)3;/h4-7H2,1-3H3;1H
Clé InChI
FPQQSJJWHUJYPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Beyond peptides, EDC HCl extends its influence to the construction of immunogens, where it covalently attaches haptens (small immune-response eliciting molecules) to carrier proteins, playing an instrumental role in vaccine research. The versatility of EDAC HCl further unfolds in its ability to modify nucleic acids, allowing for the labeling of DNA and RNA through their 5′ phosphate groups. This facilitates the visualization, tracking, and analysis of these essential molecules, contributing to advancements in nucleic acid research.
Additionally, EDAC HCl serves as a biomolecule bridge by acting as a crosslinker, connecting amine-reactive NHS-esters of biomolecules to carboxyl groups. This technique proves valuable in protein conjugation, enabling the creation of hybrid molecules with novel properties and functions. The underlying mechanism of EDAC HCl involves its reaction with a carboxyl group, forming an unstable intermediate that actively seeks an amine partner. The delicate balance of this reaction underscores the importance of optimizing conditions for efficient conjugation. The assistance of N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) further enhances EDAC HCl′s capabilities, stabilizing the intermediate and enabling two-step conjugation procedures. This additional feature provides greater flexibility and control, particularly in dealing with complex biomolecules.
Application
- for the immobilisation of trypsin onto self-assembled monolayers (SAMs)
- as a component for the preparation of collagen matrices
- for the preparation of phosphoethanolamine(PEt)-conjugated sepharose
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Caractéristiques et avantages
Autres remarques
Produit comparable
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT RE 2 Oral
Organes cibles
Stomach,large intestine,lymph node
Code de la classe de stockage
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique








![1-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]-3-ethylcarbodiimide methiodide](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/414/134/4eb9c126-d7f9-4e12-9e3a-95cb077824fd/640/4eb9c126-d7f9-4e12-9e3a-95cb077824fd.png)