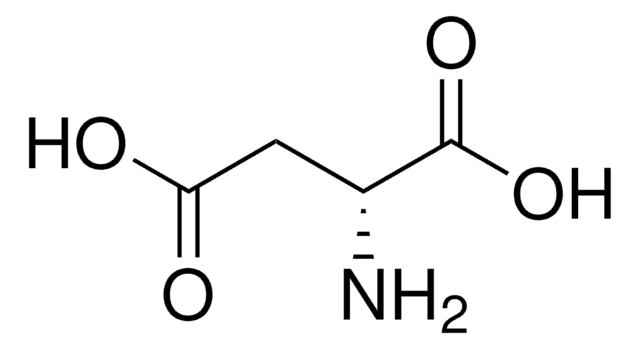
A1330000
Acide L-aspartique
European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard
Synonyme(s) :
Acide (S)-(+)-aminosuccinique, Acide (S)-aminobutanedioïque
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Qualité
pharmaceutical primary standard
Famille d'API
aspartic acid
Fabricant/nom de marque
EDQM
Pf
>300 °C (dec.) (lit.)
Application(s)
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
Format
neat
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Chaîne SMILES
N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H7NO4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m0/s1
Clé InChI
CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Conditionnement
Autres remarques
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
Si vous avez besoin d'assistance, veuillez contacter Service Clients
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Protocoles
Separation of L-Alanine; Glycine; L-Valine; L-Leucine; L-Isoleucine; L-Proline; L-Methionine; L-Serine; L-Threonine; L-Phenylalanine; L-Aspartic acid; L-4-Hydroxyproline; L-Cysteine; L-Glutamic acid; L-Asparagine; L-Lysine; L-Glutamine; L-Histidine; L-Tyrosine; L-Tryptophan; L-Cystine
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique