A8949
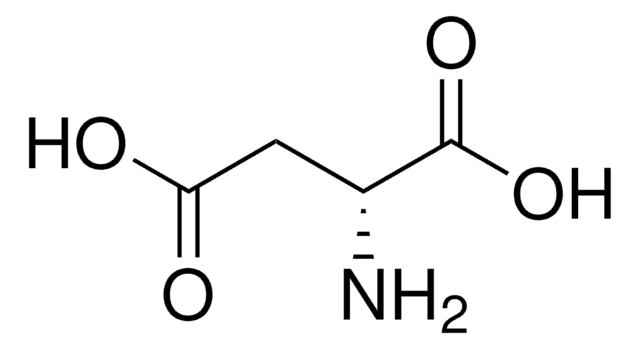
Acide L-aspartique
≥99% (HPLC), BioXtra
Synonyme(s) :
Acide (S)-(+)-aminosuccinique, Acide (S)-aminobutanedioïque
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Nom du produit
Acide L-aspartique, BioXtra, ≥99% (HPLC)
Gamme de produits
BioXtra
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥99% (HPLC)
Forme
powder
Impuretés
≤0.0005% Phosphorus (P)
≤0.1% Insoluble matter
Résidus de calcination
≤0.1%
Couleur
white to off-white
Pf
>300 °C (dec.) (lit.)
Solubilité
1 M HCl: 0.5 M, clear, colorless
Traces d'anions
chloride (Cl-): ≤0.05%
sulfate (SO42-): ≤0.05%
Traces de cations
Al: ≤0.0005%
Ca: ≤0.001%
Cu: ≤0.0005%
Fe: ≤0.0005%
K: ≤0.005%
Mg: ≤0.0005%
NH4+: ≤0.05%
Na: ≤0.005%
Pb: ≤0.001%
Zn: ≤0.0005%
Chaîne SMILES
N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H7NO4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m0/s1
Clé InChI
CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N
Informations sur le gène
human ... CA1(759) , CA2(760)
rat ... Grin2a(24409)
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Application
- Metabolomics Analysis Identifies Differential Metabolites as Biomarkers for Acute Myocardial Infarction.: Research identifies key metabolites, including L-Aspartic acid, involved in the metabolic pathways affected during acute myocardial infarction. This study enhances the understanding of biochemical changes during heart attacks, potentially leading to better diagnostic markers (Zhou et al., 2024).
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Chromatograms
application for HPLCapplication for HPLCNotre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique