SMB00801
Lipopolysaccharides from Proteus vulgaris
purified by phenol extraction
Sinônimo(s):
LPS
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Código UNSPSC:
12352211
NACRES:
NA.28
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
bacterial (Proteus vulgaris)
Nível de qualidade
Formulário
lyophilized powder
purificado por
phenol extraction
Impurezas
≤3% Protein (Lowry)
cor
white to yellow cast
solubilidade
water: 4.90-5.10 mg/mL, faintly hazy to hazy, colorless to faintly yellow
Condições de expedição
ambient
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
Descrição geral
Lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) are characteristic components of the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria. They consist of lipid A moiety linked to an antigenic O-polysaccharide.
Proteus vulgaris is a rod-shaped Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe bacterium. It inhabits the intestinal tract of humans and animals and can be found in soil, water and feces. P. vulgaris is a member of the Enterobacteriaceae family which are opportunistic pathogens in humans, responsible for urinary tract and burn infections.
The chemical structures of LPS from Proteus sp. are different from each other.
Proteus vulgaris is a rod-shaped Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe bacterium. It inhabits the intestinal tract of humans and animals and can be found in soil, water and feces. P. vulgaris is a member of the Enterobacteriaceae family which are opportunistic pathogens in humans, responsible for urinary tract and burn infections.
The chemical structures of LPS from Proteus sp. are different from each other.
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
LPS and its lipid A moiety stimulate cells of the innate immune system by the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), a member of the Toll-like receptor protein family, which recognizes common pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). Different chemical structures of LPS can be associated with the virulence and pathogenesis of the bacteria. It has been reported that the LPS chemical structure from P. vulgaris can influence the crystallization of mineral urine components (such as calcium and magnesium), resulting in stone formation in the kidney. Antibodies produced in rickettsial infections were found to react with LPS from Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis. This phenomenon allows the purified LPS from these two species to serve as a tool for the diagnosis of rickettsiosis (scrub typhus, caused by the bacterium Orientia sp.) in the Weil-Felix test.
Outras notas
To gain a comprehensive understanding of our extensive range of Lipopolysaccharides for your research, we encourage you to visit our Carbohydrates Category page.
produto relacionado
Nº do produto
Descrição
Preços
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Certificados de análise (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Não está vendo a versão correta?
Se precisar de uma versão específica, você pode procurar um certificado específico pelo número do lote ou da remessa.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
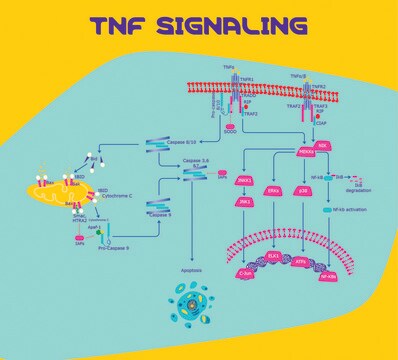
LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway
Lu, Y.C., Yeh, W.C., Ohashi, P.S.
Cytokine, 42, 145-151 (2008)
S Mizushiri et al.
Microbiology and immunology, 34(2), 121-133 (1990-01-01)
The lipopolysaccharides (LPS) extracted from Proteus strains OX2, OX19, and OXK used as antigens in the Weil-Felix test, were characterized by chemical analysis and SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). To separate the O-polysaccharide, core-oligosaccharide, and lipid A moieties, each LPS was
B Bartodziejska et al.
European journal of biochemistry, 256(2), 488-493 (1998-10-06)
The following structure of the O-specific polysaccharide chain (O-antigen) of the Proteus vulgaris 032 lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was established by 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectroscopy, including two-dimensional NOESY and H-detected 1H,13C heteronuclear multiple-quantum coherence (HMQC) experiments: -->2)-alpha-L-RhapI-(1-->2)-alpha-L-RhapII-(1-->4)-beta-D-++ +GalpA(I)-(1-->3)-beta-D-GlcpNAc-(1-->4)-alpha-D-GalpA(II)-(1-- >. In addition, an
Agnieszka Torzewska et al.
Journal of medical microbiology, 52(Pt 6), 471-477 (2003-05-16)
Formation of infectious urinary calculi is the most common complication accompanying urinary tract infections by members of the genus Proteus. The major factor involved in stone formation is the urease produced by these bacteria, which causes local supersaturation and crystallization
A Torzewska et al.
FEMS immunology and medical microbiology, 31(3), 227-234 (2001-11-27)
The O-specific polysaccharide (O-antigen) of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of Proteus vulgaris O37 was studied by (1)H and (13)C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy before and after O-deacetylation and found to be structurally similar to that of P. vulgaris O46 studied earlier.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica