E5017
Anti-LPA1, C-Terminal antibody produced in rabbit
IgG fraction of antiserum, buffered aqueous solution
Sinônimo(s):
Anti-EDG-2, Anti-Endothelial Cell Differentiation Gene 2
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
rabbit
Nível de qualidade
conjugado
unconjugated
forma do anticorpo
IgG fraction of antiserum
tipo de produto de anticorpo
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
Formulário
buffered aqueous solution
peso molecular
antigen ~50 kDa
reatividade de espécies
human, rat
técnica(s)
western blot: suitable
nº de adesão UniProt
Condições de expedição
dry ice
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
modificação pós-traducional do alvo
unmodified
Informações sobre genes
human ... LPAR1(1902)
rat ... Lpar1(116744)
Categorias relacionadas
Imunogênio
synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acids 328-344 of human EDG-2/LPA1.
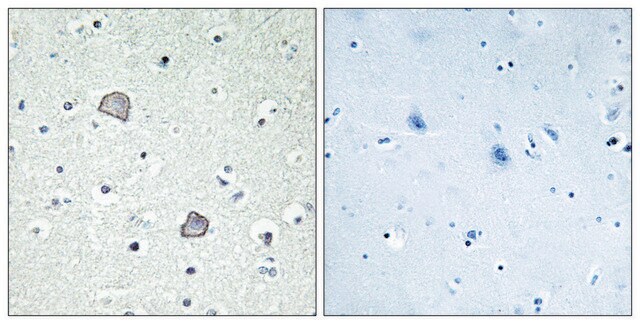
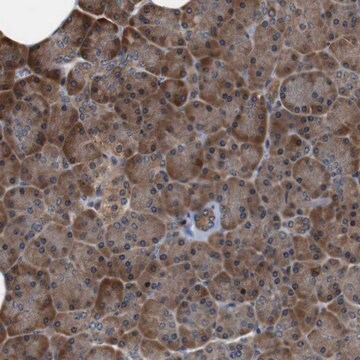
Aplicação
Anti-LPA1, C-Terminal antibody produced in rabbit is suitable for western blotting at a working dilution of 1:1000 using rat brain microsomal fraction.
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPA1) is a protein encoded by the LPAR1 gene in humans. It is constitutively localized in the nucleus of mammalian cells and may be involved in regulating intranuclear protein phosphorylation and signalling. LPA1 is differentially expressed in androgen-insensitive and LPA-responsive cells. It is not expressed in androgen-dependent and LPA-resistant cells.Its expression is significantly higher in the cancer compared with the benign tissues and may possibly act as a drug target to interfere with progression of prostate cancer. LPA1 helps in promoting cell proliferation, survival and migration by acting on cognate G protein-coupled receptors.
forma física
Solution in PBS with 0.08% sodium azide
Exoneração de responsabilidade
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Não está encontrando o produto certo?
Experimente o nosso Ferramenta de seleção de produtos.
Código de classe de armazenamento
10 - Combustible liquids
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Goetzl, E., et al.
Immunology, 162, 2049-2049 (1992)
Rishu Guo et al.
Endocrinology, 147(10), 4883-4892 (2006-07-01)
The bioactive phospholipid lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) promotes cell proliferation, survival, and migration by acting on cognate G protein-coupled receptors named LPA(1), LPA(2), and LPA(3). We profiled gene expression of LPA receptors in androgen-dependent and androgen-insensitive prostate cancer cells and found
Catherine M Waters et al.
The Biochemical journal, 398(1), 55-62 (2006-05-24)
We show that LPA1 (lysophosphatidic acid receptor-1) is constitutively localized in the nucleus of mammalian cells. LPA1 also traffics from cell membranes to the nucleus in response to LPA (lysophosphatidic acid). Several lines of evidence suggest an important role for
N Fukushima et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95(11), 6151-6156 (1998-05-30)
Extracellular lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) produces diverse cellular responses in many cell types. Recent reports of several molecularly distinct G protein-coupled receptors have raised the possibility that the responses to LPA stimulation could be mediated by the combination of several uni-functional
E J Goetzl et al.
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 12(15), 1589-1598 (1998-12-05)
The lysophospholipid (LPL) mediators lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) are generated by enzymatic cleavage of stores of glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelin, respectively, in membranes of stimulated cells. LPLs are albumin bound, distributed widely in mammalian tissues, and increased in
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica