B0806
Anti-BACE 1, C-Terminus (485-501) antibody produced in rabbit

affinity isolated antibody, buffered aqueous solution
Sinônimo(s):
Anti-β-Site APP Cleaving Enzyme
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
rabbit
Nível de qualidade
conjugado
unconjugated
forma do anticorpo
affinity isolated antibody
tipo de produto de anticorpo
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
Formulário
buffered aqueous solution
peso molecular
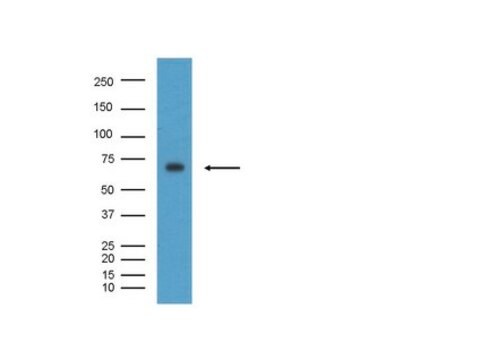
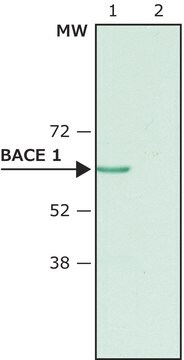
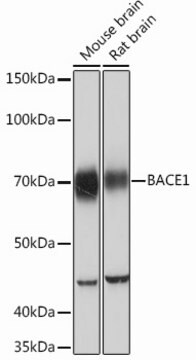
antigen 70 kDa
reatividade de espécies
human
validação aprimorada
recombinant expression
Learn more about Antibody Enhanced Validation
técnica(s)
microarray: suitable
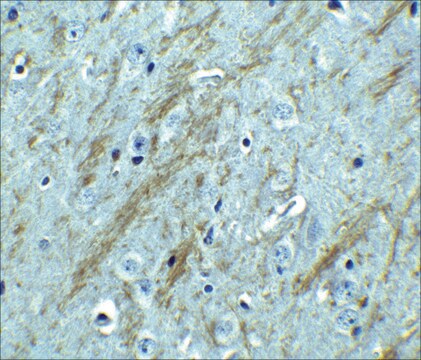
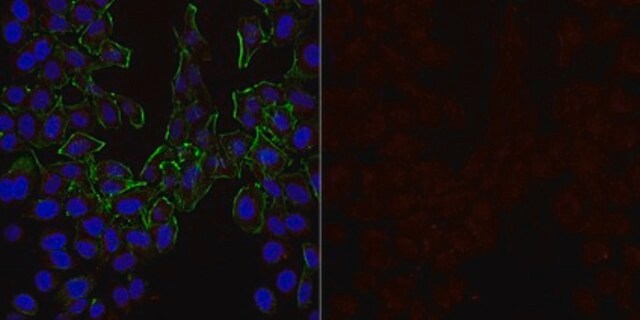
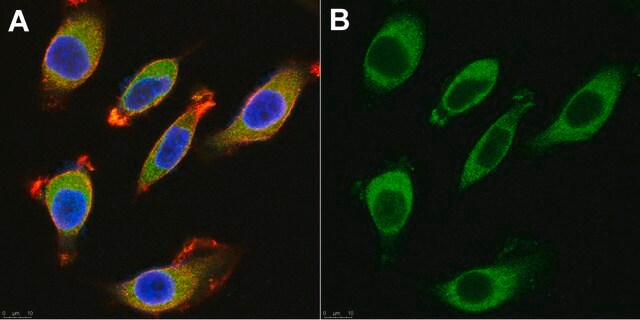
western blot: 1:1,000 using a whole cell extract from the human kidney HEK293 cell line stably transfected with human BACE-1
nº de adesão UniProt
Condições de expedição
dry ice
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
modificação pós-traducional do alvo
unmodified
Informações sobre genes
human ... BACE1(23621)
Descrição geral
Imunogênio
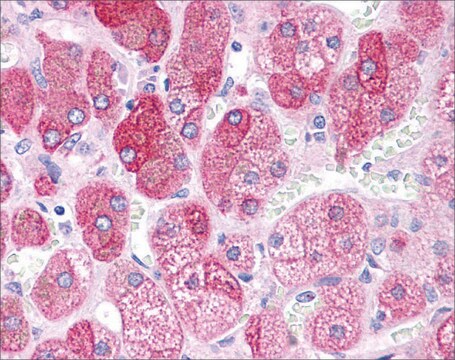
Aplicação
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
forma física
Exoneração de responsabilidade
Não está encontrando o produto certo?
Experimente o nosso Ferramenta de seleção de produtos.
Código de classe de armazenamento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
nwg
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Certificados de análise (COA)
Não está vendo a versão correta?
Se precisar de uma versão específica, você pode procurar um certificado específico pelo número do lote ou da remessa.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica