52131
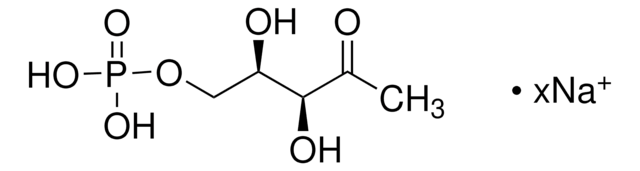
2-C-Methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate lithium salt
≥98% (TLC)
Sinônimo(s):
MEP
Faça loginpara ver os preços organizacionais e de contrato
About This Item
Fórmula empírica (Notação de Hill):
C5H11O7P · xLi+
Número CAS:
Peso molecular:
214.11 (free acid basis)
Código UNSPSC:
12352106
ID de substância PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.25
Produtos recomendados
Nível de qualidade
Ensaio
≥98% (TLC)
temperatura de armazenamento
−20°C
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
O=P(O)(O)OC[C@H](O)[C@@](O)(C)CO.C
InChI
1S/C5H13O7P/c1-5(8,3-6)4(7)2-12-13(9,10)11/h4,6-8H,2-3H2,1H3,(H2,9,10,11)/t4-,5+/m1/s1
chave InChI
XMWHRVNVKDKBRG-UHNVWZDZSA-N
Aplicação
2-C-Methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP), the product of reductoisomerase IspC and first committed MEP pathway intermediate, is used to study the non-mevalonate MEP pathway for the biosynthesis of isoprenoids. MEP is used as a precursor for the synthesis of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl D-erythritol (CDP-ME), a key intermediate of the non-mevalonate pathway.
Ações bioquímicas/fisiológicas
Metabolite intermediate specific to the non-mevalonate MEP pathway, generally found in prokaryotes, as precursor to isoprenoids as well as non-isoprenoids like vitamins. As this pathway is not present in humans, it is of interest for the development of bacterium-specific drugs in the search for treatments of infectious diseases.
Embalagem
Bottomless glass bottle. Contents are inside inserted fused cone.
Código de classe de armazenamento
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Sina I Odejinmi et al.
Tetrahedron, 68(43), 8937-8941 (2012-10-11)
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) is a key chemical intermediate of the non-mevalonate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis employed by many pathogenic microbes. MEP is also the precursor for the synthesis of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl D-erythritol (CDP-ME), another key intermediate of the non-mevalonate pathway. As this
Hyungjin Eoh et al.
Tuberculosis (Edinburgh, Scotland), 89(1), 1-11 (2008-09-17)
Tuberculosis (TB) is still a major public health problem, compounded by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-TB co-infection and recent emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug resistant (XDR)-TB. Novel anti-TB drugs are urgently required. In this context, the 2C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate
Andréa Hemmerlin et al.
Progress in lipid research, 51(2), 95-148 (2011-12-27)
When compared to other organisms, plants are atypical with respect to isoprenoid biosynthesis: they utilize two distinct and separately compartmentalized pathways to build up isoprene units. The co-existence of these pathways in the cytosol and in plastids might permit the
J Kipchirchir Bitok et al.
ACS chemical biology, 7(10), 1702-1710 (2012-07-31)
There is significant progress toward understanding catalysis throughout the essential MEP pathway to isoprenoids in human pathogens; however, little is known about pathway regulation. The present study begins by testing the hypothesis that isoprenoid biosynthesis is regulated via feedback inhibition
Sinéad Heuston et al.
Microbiology (Reading, England), 158(Pt 6), 1389-1401 (2012-04-03)
Isoprenoid biosynthesis is essential for cell survival. Over 35 000 isoprenoid molecules have been identified to date in the three domains of life (bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes), and these molecules are involved in a wide variety of vital biological functions. Isoprenoids
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica