ABT257
Anti-Pro-Collagen Type I, A1/COL1A1
from rabbit, purified by affinity chromatography
Sinônimo(s):
Pro-collagen alpha-1(I) chain, Pro-Alpha-1 type I collagen
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
fonte biológica
rabbit
Nível de qualidade
forma do anticorpo
affinity isolated antibody
tipo de produto de anticorpo
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
purificado por
affinity chromatography
reatividade de espécies
mouse, human
técnica(s)
flow cytometry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
western blot: suitable
nº de adesão NCBI
nº de adesão UniProt
Condições de expedição
wet ice
modificação pós-traducional do alvo
unmodified
Informações sobre genes
human ... COL1A1(1277)
Descrição geral
Especificidade
Imunogênio
Aplicação
Cell Structure
Adhesion (CAMs)
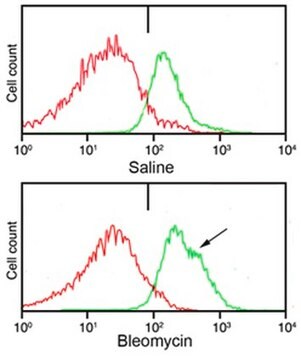
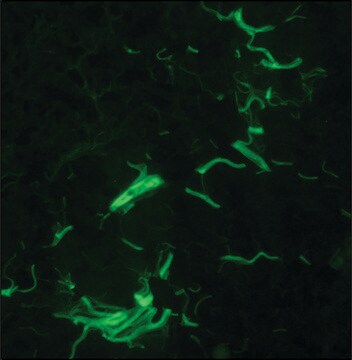
Flow Cytometry Analysis: A representative lot detected Pro-Collagen Type I, A1/COL1A1 in mouse lung tissue.
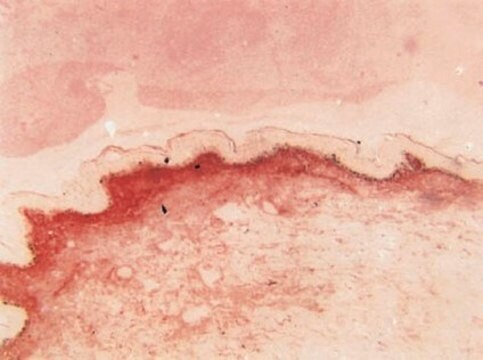
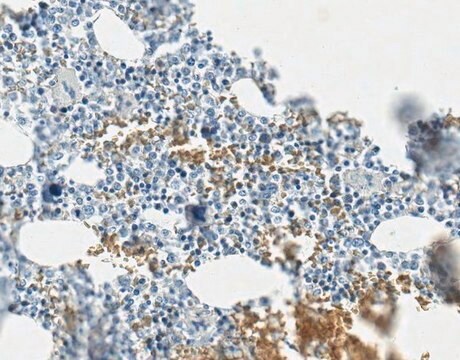
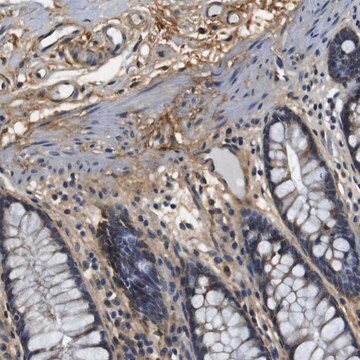
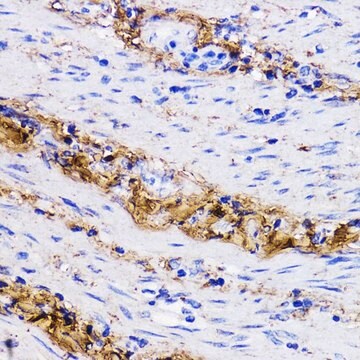
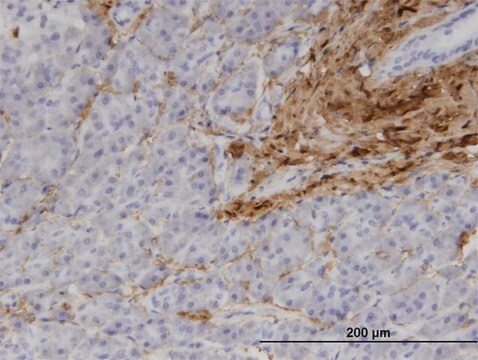
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected Pro-Collagen Type I, A1/COL1A1 in mouse lung tissue.
Qualidade
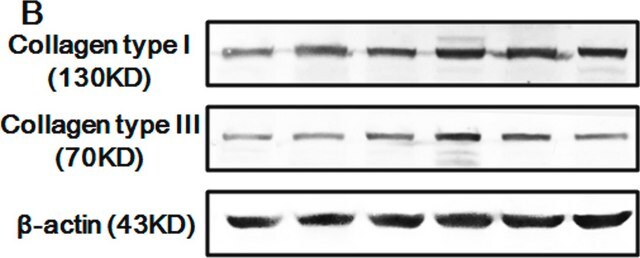
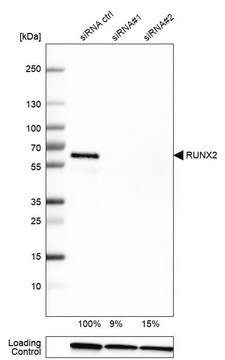
Western Blotting Analysis: A 1:500 dilution of this antibody detected Pro-Collagen Type I, A1/COL1A1 in 10 µg of mouse skin tissue lysate.
Descrição-alvo
forma física
Armazenamento e estabilidade
Outras notas
Exoneração de responsabilidade
Não está encontrando o produto certo?
Experimente o nosso Ferramenta de seleção de produtos.
Código de classe de armazenamento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 2
Certificados de análise (COA)
Busque Certificados de análise (COA) digitando o Número do Lote do produto. Os números de lote e remessa podem ser encontrados no rótulo de um produto após a palavra “Lot” ou “Batch”.
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Os clientes também visualizaram
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica