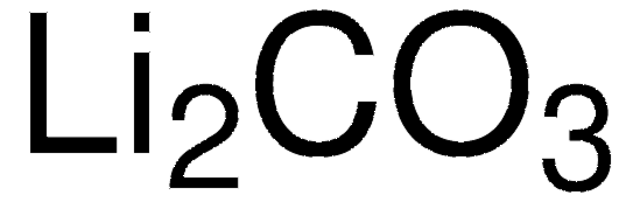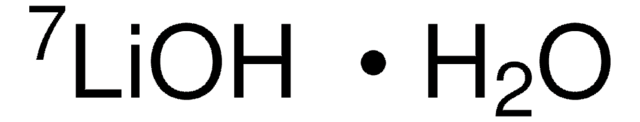930903
Lithium hydroxide monohydrate
battery grade, ≥99.9% trace metals basis
Sinônimo(s):
Lithine hydrate, Lithium hydroxide hydrate
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
Nível de qualidade
grau
battery grade
Ensaio
≥99.9% trace metals basis
Formulário
powder
características do produto alternativo mais ecológico
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Impurezas
≤1000 ppm (trace metals analysis)
pf
423 °C
solubilidade
H2O: soluble ((lit.))
ethanol: slightly soluble ((lit.))
methanol: soluble ((lit.))
traços de ânion
chloride (Cl-): ≤50 ppm
sulfate (SO42-): ≤50 ppm
aplicação(ões)
battery manufacturing
categoria alternativa mais ecológica
cadeia de caracteres SMILES
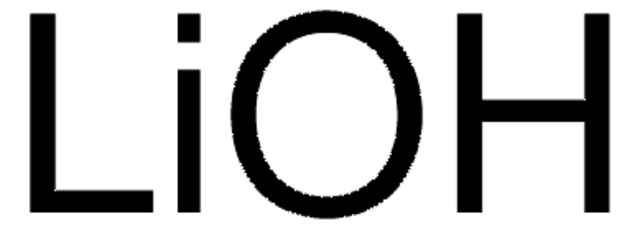
[Li+].O.[OH-]
InChI
1S/Li.2H2O/h;2*1H2/q+1;;/p-1
chave InChI
GLXDVVHUTZTUQK-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Categorias relacionadas
Descrição geral
Lithium hydroxide is produced in several ways. Most commonly, lithium carbonate is reacted with calcium hydroxide in a metathesis reaction. This directly yields lithium hydroxide hydrate, which is separated from the insoluble calcium carbonate byproduct and purified. Alternatively, when the source of lithium is spodumene ore, the ore can be converted to lithium hydroxide without first forming the carbonate. In the process, the lithium ore is treated with high-temperatures and sulfuric acid to form lithium sulfate; then the lithium sulfate is reacted with sodium hydroxide to form lithium hydroxide hydrate, which is purified.
Aplicação
Our battery grade lithium hydroxide monohydrate is well-suited for synthesis of nickel-rich metal oxides, like lithium nickel-manganese-aluminum oxide (NMA) and complex quaternary transition metal oxides like Zr-doped or Ti-doped nickel-manganese oxide.
Our lithium hydroxide monohydrate can also be used to synthesize lithium iron phosphates like LiFePO4 or lithium manganese oxides like Li2Mn2O4.
Palavra indicadora
Danger
Frases de perigo
Declarações de precaução
Classificações de perigo
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Código de classe de armazenamento
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 1
Ponto de fulgor (°F)
Not applicable
Ponto de fulgor (°C)
Not applicable
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Certificados de análise (COA)
Lamentamos, não temos COA para este produto disponíveis online no momento.
Se precisar de ajuda, entre em contato Atendimento ao cliente
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica