915025
TissueFab® bioink Bone
UV/365 nm
Sinônimo(s):
3D Bioprinting, Bioink, GelMA, TissueFab
About This Item
Produtos recomendados
descrição
0.2 μm sterile filtered
suitable for 3D bioprinting applications
Nível de qualidade
Formulário
gel form (viscous)
Impurezas
≤5 CFU/g Bioburden (Fungal)
≤5 CFU/g Bioburden (Total Aerobic)
cor
white
pH
6.5-7.5
aplicação(ões)
3D bioprinting
temperatura de armazenamento
2-8°C
Procurando produtos similares? Visita Guia de comparação de produtos
Aplicação
Informações legais
Código de classe de armazenamento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de risco de água (WGK)
WGK 3
Escolha uma das versões mais recentes:
Certificados de análise (COA)
Lamentamos, não temos COA para este produto disponíveis online no momento.
Se precisar de ajuda, entre em contato Atendimento ao cliente
Já possui este produto?
Encontre a documentação dos produtos que você adquiriu recentemente na biblioteca de documentos.
Nossa equipe de cientistas tem experiência em todas as áreas de pesquisa, incluindo Life Sciences, ciência de materiais, síntese química, cromatografia, química analítica e muitas outras.
Entre em contato com a assistência técnica




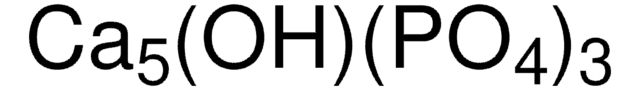
![Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid] natural origin](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/129/476/7d1c924b-f644-4889-a2d6-d7a923ce382c/640/7d1c924b-f644-4889-a2d6-d7a923ce382c.png)

